Fuel Cells Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe fuel-cell sector shows clear commercial momentum: the internal trend data reports a 2025 market size of USD 11.07 billion and a strong projected CAGR trajectory, indicating rapid near-term expansion and shifting application mix Grand View Research.
This article was last updated 83 days ago. If you find any info is missing, let us know!
Topic Dominance Index of Fuel Cells
The Dominance Index of Fuel Cells looks at the evolution of the sector through a combination of multiple data sources. We analyze the distribution of news articles that mention Fuel Cells, the timeline of newly founded companies working in this sector, and the share of voice within the global search data
Key Activities and Applications
- Data-center and critical-load backup power — customers replace diesel gensets with fuel-cell UPS and hybrid systems to reduce onsite emissions and meet stricter sustainability procurement rules StartUs Insights.
- Stationary distributed generation and microgrids (including CHP) — modular stacks and SOFC deployments target commercial, industrial and utility customers seeking resilient baseload and heat capture.
- Heavy-duty transportation (trucks, buses, rail, marine) — long-range fleets adopt high-power PEM and modular stack designs where battery solutions face range or refueling-time limits Mordor Intelligence.
- Portable and remote power (drones, UAVs, field generators) — lightweight stacks and integrated fuel processors increase endurance for UAVs and remote generators used in construction, mining and emergency response.
- On-site hydrogen and methanol-to-hydrogen generation — to avoid costly transport logistics, operators deploy reformers and electrolyzers co-located with fuel-cell systems for steady supply.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Market re-segmentation toward stationary and infrastructure use cases: transport historically dominated revenue, but fast growth in data-center UPS and distributed generation is changing demand composition.
So what: buyers with high availability requirements create a predictable first wave of large, bankable projects that de-risk manufacturing scale-up. - Technology bifurcation — PEMFC remains revenue leader for mobility and many stationary uses while SOFC and high-temperature solutions grow fastest for fuel flexibility and higher efficiency.
So what: product road maps should treat PEM and SOFC as complementary markets with different margin and integration models. - Component and materials innovation as the primary cost lever — MEA manufacturing, catalyst loading reductions and bipolar-plate automation drive unit-cost declines and manufacturing throughput gains.
So what: investors and OEMs seeking durable margin advantages should prioritize secured supply or proprietary IP in MEA, catalyst and bipolar plate lines. - Decentralized hydrogen and fuel flexibility reduce distribution friction — on-site methanol reforming and modular electrolyzers lower the practical barrier to deployment in regions lacking refueling networks.
So what: business models that bundle onsite fuel supply with service contracts improve total cost of ownership and accelerate procurement decisions. - Policy and infrastructure remain gating variables — subsidies, hydrogen hubs and refueling build-outs materially influence project economics and regional roll-outs Precedence Research market commentary.
So what: commercial roll-out timelines should map tightly to local policy windows and hub development plans.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) — low-temperature, high-power-density systems favored for mobility and many stationary UPS applications; ongoing work focuses on platinum reduction and MEA manufacturing scale.
- Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) and high-temperature stacks — deliver higher electrical efficiency and fuel flexibility for large stationary and CHP installations; material durability and thermal management are primary engineering priorities.
- MEA and catalyst engineering — advanced coating, roll-to-roll MEA manufacturing and platinum-reduction chemistries form the central cost-reduction pathway.
- Modular stack architectures and plug-and-play system integration — standardized modules for rapid field installation reduce BOS (balance-of-system) and commissioning time.
- Hybrid energy management (fuel cell + battery + controls) — systems use batteries for transient loads and fuel cells for steady state to optimize efficiency and extend stack life.
Fuel Cells Funding
A total of 975 Fuel Cells companies have received funding.
Overall, Fuel Cells companies have raised $156.6B.
Companies within the Fuel Cells domain have secured capital from 3.6K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Fuel Cells companies over the last 5 years
Fuel Cells Companies
- SinoHyKey — a specialist in MEA and CCM process improvements that claims major cost cuts for catalyst-coated membranes; the company targets component supply for OEM integrators and positions its technology to reduce per-unit MEA cost and improve power density.
- Hysata — developer of an electrolyzer architecture focused on high-efficiency green hydrogen production with the explicit aim of lowering hydrogen feedstock costs for fuel-cell systems and enabling sub-$2/kg targets for green hydrogen.
- Genevos — maritime-focused integrator producing hydrogen fuel-cell systems for ferries and workboats; it emphasizes shipboard certification and system packaging for marine retrofit projects.
- Hydroplane — small systems and powerplant developer working on fuel-cell powerplants and receiving government SBIR support for military and resilience applications; focuses on modular SOFC designs for distributed power.
- Falcon Fuel Cells (example commercial micro/portable developer) — builds lightweight PEM modules for UAVs and portable generators; the company emphasizes reduced platinum loading and compact fuel-processor integration for endurance markets.
Uncover actionable market insights on 5.5K companies driving Fuel Cells with TrendFeedr's Companies tool.
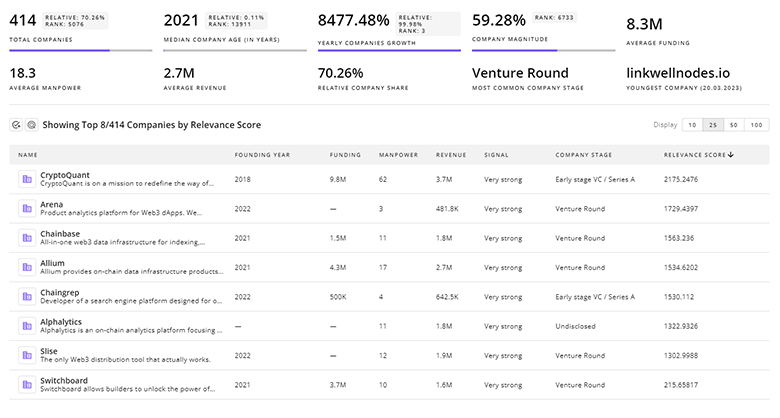
5.5K Fuel Cells Companies
Discover Fuel Cells Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Fuel Cells Investors
Get ahead with your investment strategy with insights into 3.2K Fuel Cells investors. TrendFeedr’s investors tool is your go-to source for comprehensive analysis of investment activities and financial trends. The tool is tailored for navigating the investment world, offering insights for successful market positioning and partnerships within Fuel Cells.
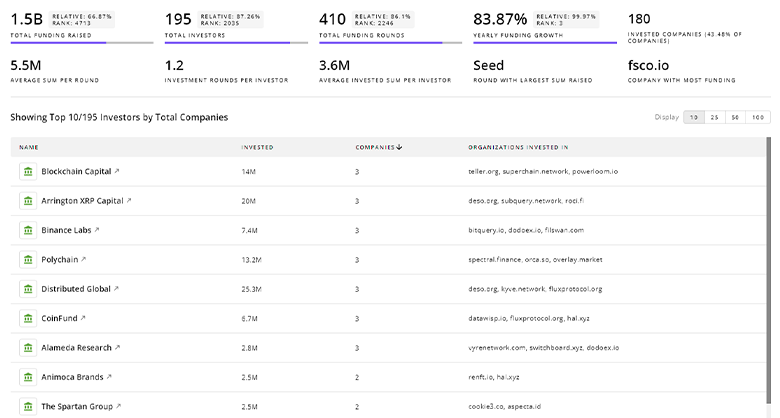
3.2K Fuel Cells Investors
Discover Fuel Cells Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Fuel Cells News
TrendFeedr’s News feature offers access to 22.8K news articles on Fuel Cells. The tool provides up-to-date news on trends, technologies, and companies, enabling effective trend and sentiment tracking.
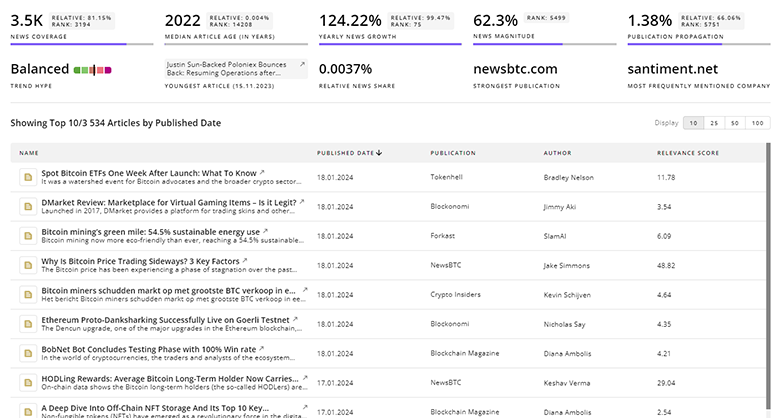
22.8K Fuel Cells News Articles
Discover Latest Fuel Cells Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Fuel cells are moving from isolated demonstrations to commercially repeatable projects where hydrogen availability, component cost and policy alignment determine winners. Near-term commercial demand concentrates on resilient stationary power (data centers, CHP, microgrids) and heavy-duty transport; both create scale opportunities for manufacturers that secure MEA and catalyst advantages and pair systems with onsite fuel solutions. Practical commercial strategy therefore combines (1) technology differentiation at the MEA and stack level, (2) vertically aligned fuel supply or on-site generation, and (3) service-centric deployment models (long-term maintenance and fuel agreements) that convert early projects into predictable revenue streams. The firms that integrate across these three dimensions will shape how quickly fuel cells capture enterprise and utility power markets.
Have expertise in trends or technology? Your input can enrich our content — consider collaborating with us!