Urban Logistics Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe urban logistics market is valued at USD 25.7 billion (2023) and the internal data projects growth to USD 77.9 billion by 2033 at a 12% CAGR, driven by e-commerce density, micro-fulfilment adoption and fleet electrification that compress delivery distances and unit costs. Rapid platform consolidation and the rise of local consolidation hubs change economics of last-mile delivery, while city-level emissions policy accelerates demand for light electric vehicles and cargo bikes, shifting capital and operational priorities for carriers and real-estate owners.
119 days ago, we last updated this report. Notice something that’s not right? Let’s fix it together.
Topic Dominance Index of Urban Logistics
The Topic Dominance Index offers a holistic analysis of Urban Logistics, merging data from 3 diverse sources: relevant published articles, newly founded companies, and global search metrics.
Key Activities and Applications
- Last-mile fulfilment from urban micro-fulfilment centres and micro-hubs: small, automated facilities placed inside or near dense urban cores to enable same-day and sub-hour fulfilment; these reduce vehicle miles traveled per parcel and support mixed-mode final-mile dispatch.
- Consolidation and transloading (Urban Consolidation Centres): central points that aggregate multi-carrier loads and reassign to low-emission local fleets, lowering inner-city truck trips and curbside pressure.
- Light-electric vehicle fleets and cargo bikes for dense cores: purpose-built Class 1–3 vehicles and e-cargo bikes that handle high-frequency, low-weight parcel flows where vans are inefficient.
- Autonomous sidewalk robots and BVLOS drones for constrained deliveries: small autonomous pods and drone links for hospital, retail and high-rise deliveries that avoid curb congestion and parking constraints automated-deliveries.com.
- Route orchestration and multi-carrier TMS for parcel shipping: cloud multi-carrier routing, real-time rate shopping and control-tower visibility to minimize cost-per-delivery and reduce failed-delivery attempts.
- Parcel locker and PUDO networks to consolidate customer collection: dense locker networks and PUDO points that reduce home-delivery inefficiency and failed-attempt costs while enabling carrier consolidation Lockars.
Key implication: shifting inventory closer to demand (micro-fulfilment + lockers) plus smarter orchestration compresses marginal last-mile cost and creates defensible service tiers for platform providers.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Platform consolidation and "ingredients" economics: larger TMS/orchestration platforms absorb or integrate specialist modules (route-optimisers, locker networks, micro-hub ops). Specialist vendors must position as integrable API ingredients or face marginalization by platform bundling Logistyx Technologies (now part of E2open).
So what: buyers prefer single-pane orchestration; vendors should prioritize API-first, composable products to access scale. - Electrification focused on the last mile: city regulation and carbon targets push carriers toward e-vans, modular EV platforms and e-cargo bikes; electrification reduces per-parcel emissions and operating cost volatility.
So what: fleet CAPEX and depot charging become strategic levers; fleet financing and EV-as-a-Service models will expand. - Micro-mobility captures dense urban volume: projections and pilots show cargo bikes taking significant parcel share in dense metros, improving curb access and lowering delivery footprint.
So what: carriers must redesign parcel sizing, packaging and sorting to exploit micro-mobility efficiencies. - Automation shifts from pilots to operational pilots at scale: autonomous pods, sidewalk robots, middle-mile driverless shuttles and BVLOS drone corridors advance from demonstration to limited commercial rollouts, changing cost structure in specific corridors antwork.link.
So what: regulatory partnerships and local infrastructure (vertiport, locker interfaces) become gating factors for scale. - Urban space management becomes a logistics asset class: curb management, micro-hub real estate and rooftop/indoor fulfilment sites emerge as scarce, high-value assets that determine delivery economics.
So what: real-estate and logistics investors will shift capital toward flexible urban industrial assets with multi-tenant micro-fulfilment capability.
Technologies and Methodologies
- AI/ML route and demand optimization: real-time dispatch engines and demand forecasting cut travel time and idle capacity; these systems generate measurable savings and emission reductions when integrated with live traffic and inventory data.
- IoT and parcel self-awareness: sensors on packages and assets deliver condition, location and handling data that feed predictive routing, exception management and SLA verification InLoop Network.
- Autonomous delivery stacks (AMR + drone + retrofit autonomy): modular autonomy (robotics navigation, SLAM, L4 middle-mile systems and retrofit kits) lets operators deploy across varied urban topologies NuPort Robotics.
- Micro-fulfilment automation and ASRS: compact automated storage and retrieval systems enable high throughput in small footprints, enabling same-day windows without large warehouses.
- Digital twins and simulation for city pilots: virtual replicas let planners test consolidation hub placement, curb allocation and autonomous routes without expensive physical pilots.
- Open API and composable orchestration: TMS/TaaS platforms win when they expose integrable components (routing, carrier selection, locker APIs), enabling an ecosystem of specialised "ingredients" to assemble tailored city solutions.
Urban Logistics Funding
A total of 174 Urban Logistics companies have received funding.
Overall, Urban Logistics companies have raised $25.7B.
Companies within the Urban Logistics domain have secured capital from 755 funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Urban Logistics companies over the last 5 years
Urban Logistics Companies
- CityFreighter — CityFreighter develops modular, light-duty electric commercial vehicles tailored for dense last-mile operations and integrates vehicle design with fleet-level backend systems to fit operator workflows; its modular chassis approach targets fleet customisation that large OEMs do not easily provide, aiming to lower TCO for urban routes where cycle lengths and access constraints dominate.
- Fernhay Solutions — Fernhay supplies zero-emission last-mile equipment (eQuad, eWalker and modular Cube containers) and focuses on tight-street deliveries where vans cannot reach; the compact payload concept (≈200kg containers) supports retailers and carriers that need dense drop densities with low footprint and reduced curb time.
- Neubility — Neubility operates autonomous sidewalk delivery robots and an on-demand robot fleet platform designed for high-pedestrian cities; the company targets continuous operation in dense downtown environments by combining visual SLAM navigation with an on-demand service model to avoid geo-fencing limits typical of earlier pilots.
- MicroHUB Riviera — MicroHUB develops micro-hub networks that transload cartons from trucks to cargo bikes for last-mile distribution in Swiss towns; the non-profit model focuses on local consolidation, reducing truck trips and serving as a testbed for city partnerships and information exchange platforms.
- LogisticsOS — LogisticsOS supplies a high-performance route-optimization API targeted at last-mile operators and delivery apps; its engine emphasizes dense route clustering, fast compute times and linear scaling, enabling drivers to remain local and lowering total travel time by a reported 10–20% versus legacy optimisers.
(Each description above references company profiles in the available company dataset: CityFreighter, Fernhay, Neubility, MicroHUB Riviera, LogisticsOS).
Stay connected with industry movements through TrendFeedr’s Companies tool, which covers 579 Urban Logistics companies.
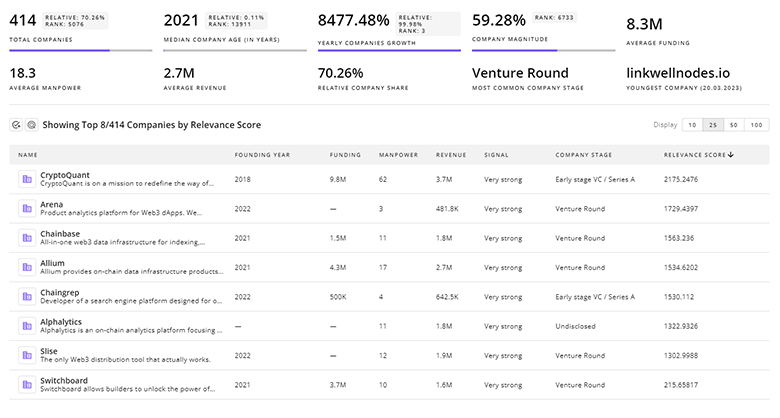
579 Urban Logistics Companies
Discover Urban Logistics Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Urban Logistics Investors
Discover investment patterns and trends with TrendFeedr’s Investors tool based on insights into 954 Urban Logistics investors. This tool is essential for understanding the financial ecosystem of Urban Logistics and developing successful investment strategies.
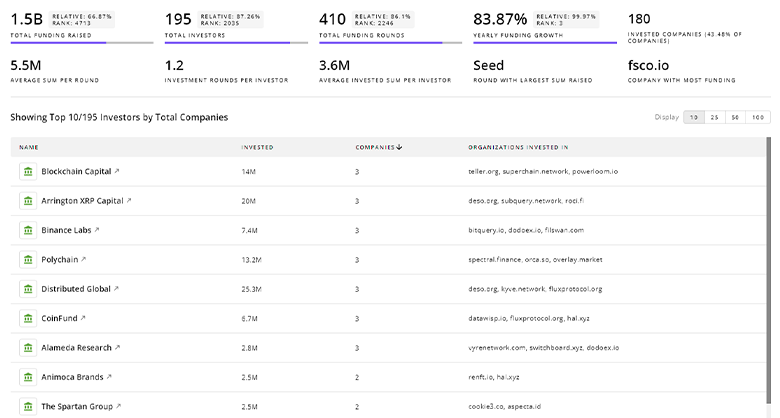
954 Urban Logistics Investors
Discover Urban Logistics Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Urban Logistics News
TrendFeedr’s News feature grants you access to 1.1K Urban Logistics articles. This tool supports professionals in tracking both past trends and current momentum in the industry.
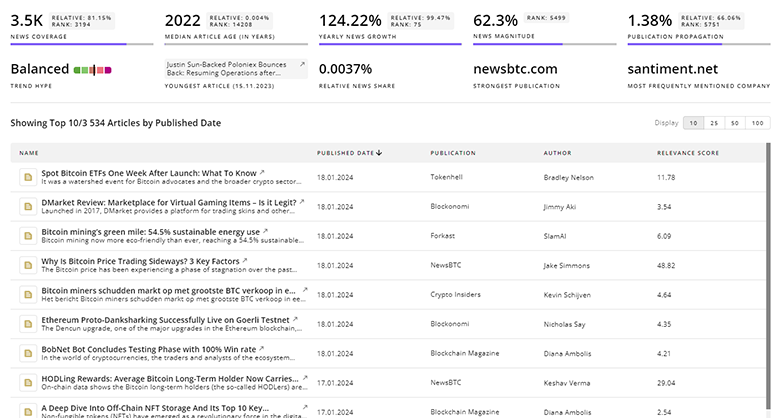
1.1K Urban Logistics News Articles
Discover Latest Urban Logistics Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Urban logistics is shifting from isolated operational fixes to integrated systems that combine local inventory, low-emission vehicles and data orchestration. Firms that align product design with city constraints (curb access, micro-fulfilment footprints, charging and parking), expose clean, composable APIs for platform partners and prove verifiable emissions and cost improvements will capture the most attractive margins. Investors should treat urban real-estate (micro-hubs and curb slots), fleet electrification services and orchestration software as the primary levers to scale profitable last-mile networks while monitoring regulatory windows and component supply risks that can change unit economics quickly.
We're looking to collaborate with knowledgeable insiders to enhance our analysis of trends and tech. Join us!