Antimicrobial Resistance Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe global antimicrobial resistance (AMR) challenge is intensifying, driven by diagnostic shortfalls, persistent high resistance in priority pathogens, and concentrated investment in rapid-testing and alternative therapeutics: the rapid AST topic alone has attracted $1.36B in total funding and involves 121 active companies. Surveillance data show alarming population-level resistance — for example, recent WHO analysis reports that one in six laboratory-confirmed infections were resistant in 2023, with resistance rising in >40% of monitored pathogen–drug combinations between 2018–2023 Global antibiotic resistance surveillance report 2025. The net effect is a market and policy environment that prizes speed-to-result, environmental surveillance, and mechanism-agnostic therapeutic approaches (phages, peptides, adjuvants) because delaying targeted therapy increases mortality, costs, and selective pressure for further resistance.
This report was last updated yesterday. Spot an error or missing detail? Help us fix it by getting in touch!
Topic Dominance Index of Antimicrobial Resistance
To identify the Dominance Index of Antimicrobial Resistance in the Trend and Technology ecosystem, we look at 3 different time series: the timeline of published articles, founded companies, and global search.
Key Activities and Applications
- Rapid antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) — Clinical and near-patient systems compress time-to-result from days to hours (and in some platforms, minutes), enabling same-shift therapy changes and reducing inappropriate broad-spectrum antibiotic use.
- Phenotypic and growth-independent assays — Platforms that measure single-cell motion, metabolic activity, or physical responses deliver actionable susceptibility without multi-day culture steps, addressing sepsis and bloodstream infection workflows.
- Genotypic resistance detection and resistome mapping — High-throughput nucleic acid assays and environmental eDNA surveillance identify resistance genes across clinical, agricultural, and wastewater reservoirs to inform One Health interventions.
- Antimicrobial stewardship (AMS) software and decision support — EMR-integrated AI systems deliver empiric-therapy guidance, dosing optimization, and formulary enforcement to reduce misuse and guide escalation when diagnostics return.
- Non-traditional therapeutics and adjuvants — Efforts focus on phage therapies, antimicrobial peptides, β-lactamase inhibitors/adjuvants, and patho-blocking agents that reduce virulence rather than promote bactericidal selection pressure.
- Environmental surveillance and One Health monitoring — Wastewater and agricultural surveillance generate early warning signals for emergent resistance and enable targeted interventions in regions where clinical surveillance remains weak.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Diagnostic-first investment thesis — Capital and policy attention concentrate on technologies that deliver susceptibility within a clinical shift because rapid data materially change prescribing and outcomes; this is reflected in accelerating funding to AST and rapid ID platforms.
- Shift from detection to prescription intelligence — The competitive edge moves to solutions that not only detect resistance but integrate with stewardship systems and therapeutic supply chains to close the identify→treat loop Pattern Bioscience.
- Hybrid phenotypic/genotypic approaches gain traction — Combining genetic markers with rapid phenotypic readouts reduces false negatives from non-canonical resistance (tolerance, persistence, biofilms) and shortens time to accurate therapy.
- Algorithmic forecasting and policy inertia — Advanced ML models (LSTM and other approaches) improve short-term AMR forecasts but analyses indicate many national action plans have not yet produced measurable global reductions, creating a gap between predictive capability and policy enforcement.
- Commercialization of alternative modalities — Phage platforms, peptide therapeutics, and adjuvants are moving from compassionate-use/early trials to scaled manufacturing and regulatory pathways, reducing reliance on de novo small-molecule antibiotic discovery.
- Environmental co-selection recognition — Evidence that heavy metals, disinfectants, and wastewater effluent co-select for ARGs means remediation and infrastructure investments will become part of AMR strategy and procurement criteria Antibiotic Resistance Genes in Food Animal Production.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Nanomotion and single-cell phenotyping — Movement-based detection provides ultra-rapid phenotypic AST in minutes, enabling actionable results for sepsis management.
- Automated microfluidics and lab-on-chip AST — Nanofluidic and microchannel platforms cut reagent volumes and time-to-answer for bloodstream and UTI testing, supporting point-of-care deployment.
- Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) and targeted PCR panels — WGS provides high-resolution surveillance and outbreak tracing; targeted real-time arrays and SmartChip-PCR support resistome mapping in environmental samples.
- Machine learning for resistance prediction and stewardship — LSTM and other time-series models forecast resistance trends; clinical ML integrates phenotypic/genotypic results with host data to recommend therapy Global prediction of antimicrobial resistance trends using statistical and machine learning models.
- Phage engineering and rapid phage matching libraries — Automated phage selection pipelines and in-house cGMP manufacture shorten time to personalized phage cocktails for difficult infections Armata Pharmaceuticals, Inc..
- β-lactamase inhibitors and resistance-breaking adjuvants — Small-molecule and biologic adjuvants restore susceptibility of legacy antibiotics and offer a lower-capital risk path to clinical value.
- Environmental eDNA surveillance and wastewater metagenomics — Routine eDNA sampling supplies population-level resistance indicators that inform regional interventions and antimicrobial stewardship.
Antimicrobial Resistance Funding
A total of 380 Antimicrobial Resistance companies have received funding.
Overall, Antimicrobial Resistance companies have raised $30.1B.
Companies within the Antimicrobial Resistance domain have secured capital from 1.6K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Antimicrobial Resistance companies over the last 5 years
Antimicrobial Resistance Companies
- Resistell — Resistell commercializes nanomotion-based ultra-rapid AST that detects bacterial movement changes to report susceptibility in minutes; the device targets sepsis and bloodstream infection workflows and positions itself as a phenotypic, growth-independent alternative to culture-based antibiograms. Resistell holds Series B funding and emphasizes rapid decision support to reduce ineffective empiric therapy. Its small footprint and rapid time to result make it attractive to hospital labs seeking same-shift answers for critical infections.
- PathoBlock — PathoBlock develops antivirulence (patho-blocking) therapeutics that neutralize bacterial pathogenicity rather than kill organisms, aiming to reduce selective pressure and slow resistance emergence; its lead programs focus on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and early-stage translational validation has emphasized reduced host damage and lower resistance risk. The approach targets prophylactic and adjunctive use in high-risk wards, presenting a regulatory and stewardship-friendly value proposition.
- Parx Materials — Parx Materials offers a biomimetic, biocide-free surface technology that prevents microbial adhesion and biofilm formation without releasing biocides, aiming to reduce hospital-acquired infection risk and avoid environmental co-selection pressures that foster ARG persistence; the technology targets medical devices and high-touch infrastructure where continuous protection reduces infection vectors. This non-pharmaceutical intervention appeals to infrastructure buyers that must balance infection control with long-term ecological risk.
- AdjuTec Pharma AS — AdjuTec Pharma develops β-lactamase inhibitors/adjuvants intended to restore activity of widely used antibiotics; the company’s lead candidate entered clinical development to start addressing carbapenem and ESBL threats, offering a shorter path to clinical utility by augmenting approved agents rather than pursuing de novo antibiotic chemistry. The model reduces R&D risk and fits stewardship strategies that prefer preserving existing effective agents.
- Resistomap — Resistomap provides environmental surveillance services using high-throughput qPCR/eDNA platforms for wastewater and ecosystem resistome monitoring; its datasets support regional risk mapping, evaluate intervention impact, and feed public health dashboards for One Health AMR programs. By linking environmental signals to clinical events, Resistomap creates a market for subscription surveillance and consulting to governments and large agricultural clients.
Identify and analyze 1.3K innovators and key players in Antimicrobial Resistance more easily with this feature.
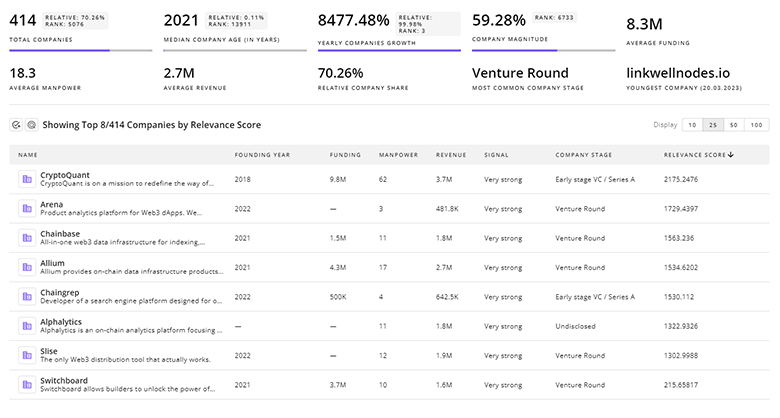
1.3K Antimicrobial Resistance Companies
Discover Antimicrobial Resistance Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Antimicrobial Resistance Investors
TrendFeedr’s investors tool offers a detailed view of investment activities that align with specific trends and technologies. This tool features comprehensive data on 1.4K Antimicrobial Resistance investors, funding rounds, and investment trends, providing an overview of market dynamics.
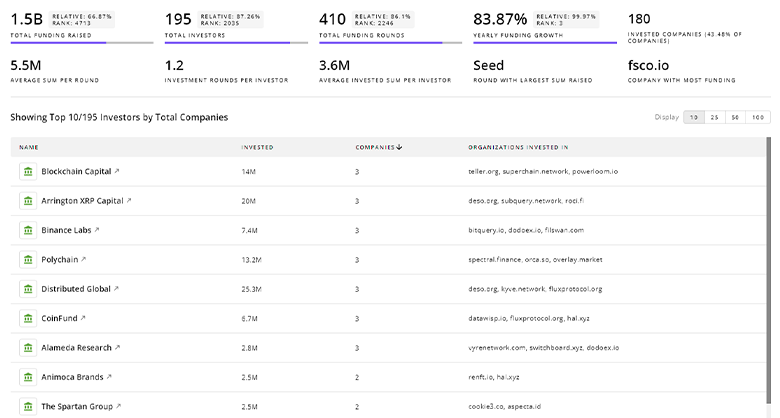
1.4K Antimicrobial Resistance Investors
Discover Antimicrobial Resistance Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Antimicrobial Resistance News
Stay informed and ahead of the curve with TrendFeedr’s News feature, which provides access to 7.0K Antimicrobial Resistance articles. The tool is tailored for professionals seeking to understand the historical trajectory and current momentum of changing market trends.
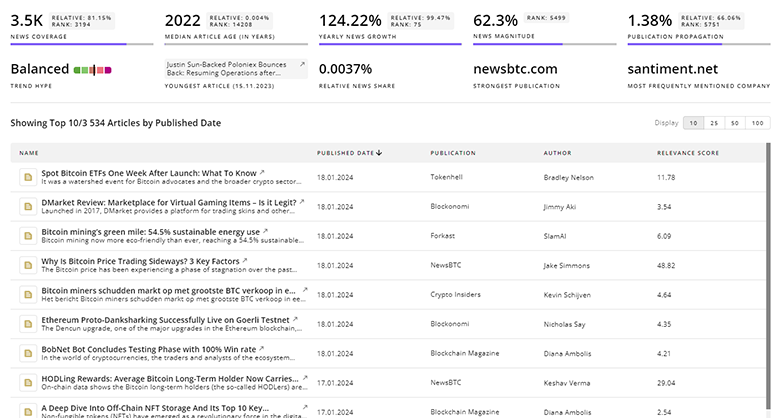
7.0K Antimicrobial Resistance News Articles
Discover Latest Antimicrobial Resistance Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
The AMR landscape is defined by an urgent clinical need and a clear market signal: speed and integration beat single-point innovation. Rapid AST and integrated stewardship platforms create immediate clinical value by changing prescribing behavior; environmental surveillance and One Health data provide the strategic inputs necessary to prioritize interventions geographically and sectorally. Therapeutic innovation is migrating away from high-cost, high-risk antibiotic discovery toward pragmatic pathways—adjuvants, engineered phages, peptides, and antivirulence agents—that can be paired with diagnostics and stewardship to preserve efficacy. For business leaders and health systems, the practical plays are clear: invest where diagnostic speed meets decision support, partner across clinical and environmental surveillance silos, and favor therapeutic approaches that lower selective pressure while enabling scalable manufacturing and regulatory pathways.
Interested in enhancing our coverage of trends and tech? We value insights from experts like you - reach out!