Autonomous Delivery Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe autonomous delivery market is at an inflection point: global market data places the sector at $1.85 billion in 2024 with an expected rise to $8.68 billion by 2029, evidence that investors and operators face a near-term window to prove unit economics at scale. This report integrates market forecasts, deployment signals, and company-level activity to show that (1) ground-based last-mile robots and middle-mile autonomous trucks are splitting investment flows, (2) teleoperation plus modular retrofit stacks are the pragmatic path to commercialization, and (3) securing the final customer handoff (secure receptacles, verified access) determines whether deployments scale beyond pilots.
This report was last updated 37 days ago. Spot an error or missing detail? Help us fix it by getting in touch!
Topic Dominance Index of Autonomous Delivery
To identify the Dominance Index of Autonomous Delivery in the Trend and Technology ecosystem, we look at 3 different time series: the timeline of published articles, founded companies, and global search.
Key Activities and Applications
- Last-mile urban delivery (sidewalk and curb): Small electric bots and low-speed vehicles handling food, groceries, and parcels inside geofenced neighborhoods and campuses. These deployments prioritize lightweight payloads (≤10 kg) and dense routing to reduce human driver costs and improve frequency.
- Middle-mile B2B short-haul: Light/medium trucks running fixed short-haul routes between fulfillment centers and urban hubs—reduces reliance on long-haul drivers and concentrates safety validation in constrained corridors Gatik.
- Campus, hospital and indoor logistics: Autonomous service robots and AMRs handling internal transfers (meals, meds, supplies), where controlled environments and defined routes produce strong ROI and rapid adoption via RaaS contracts Relay Robotics.
- Micro-fulfillment to hyperlocal hand-off: Linking micro-fulfillment or dark stores to neighborhood robots or drone/rovan hand-offs reduces last-mile miles per order and shortens delivery windows; orchestration software becomes the critical glue.
- Specialized sensitive-cargo deliveries: Medical and cold-chain deliveries (blood, vaccines) by aerial drones or tightly controlled ground robots where regulatory support and BVLOS approvals are accelerating pilots.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Platform divergence — hardware vs orchestration: Two commercial strategies are emerging: companies that sell/operate robot fleets and companies that provide hardware-agnostic orchestration for mixed fleets. The latter capture long-term value if they integrate teleops, fleet analytics and ERP hooks LMAD.
- Demand economics are tightening: investors now favor demonstrable revenue per deployed unit and measurable investment efficiency, shifting later-stage capital toward operators that show consistent unit margins rather than pure R&D burn DeliverLogic.
- Endpoint security defines adoption: patents and deployment activity highlight that secure, credentialed access (lockable compartments, user verification) is the gating variable for consumer acceptance and retailer contracts.
- Teleoperation as a practical bridge: Remote human oversight reduces edge-case aborts and supports regulatory acceptance while autonomy matures in mixed traffic zones.
- Payload segmentation matters: the market splits into light (≤5 kg), medium (5–20 kg), and heavy (>20 kg) classes; most current demand clusters in the 10–50 kg band for retail parcels, shaping robot chassis and battery design Autonomous Last Mile Delivery Market Report.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Sensor fusion and map-light perception: Multi-sensor stacks (cameras, radar, selective LiDAR) combined with local BEV-style perception reduce reliance on brittle HD map maintenance and lower deployment friction in new geographies.
- Retrofit autonomy stacks: Plug-and-play autonomy modules that convert existing micro-EVs and compact vans into semi/Level-4 capable fleets offer a capital-efficient roll-out model for logistics operators Telebotics.
- AI routing + fleet reinforcement learning: Fleet managers use ML to optimize batch assignments, dynamic rebalancing, and to learn safety margins from teleoperation interventions, improving ETA performance and utilization.
- Modular payload and swappable energy systems: Modular cargo pods and swappable battery packs shorten downtime and enable mixed payload strategies across dayparts, boosting per-unit economics.
- Secure endpoint hardware and digital credentialing: Lockable multi-compartment designs, QR/OTP access, and audit logs are being standardized as procurement requirements for retailers and healthcare customers.
Autonomous Delivery Funding
A total of 155 Autonomous Delivery companies have received funding.
Overall, Autonomous Delivery companies have raised $18.5B.
Companies within the Autonomous Delivery domain have secured capital from 751 funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Autonomous Delivery companies over the last 5 years
Autonomous Delivery Companies
- Vaive Logistics — Vaive is a Barcelona-based operator building autonomous urban last-mile robots and related service layers focused on goods movement in dense city centers. Their model emphasizes a service approach (robot operation + logistics integration) rather than pure hardware sales, aiming to minimize client capital outlay while delivering lower per-drop costs in urban corridors.
- Clevon — Clevon develops lightweight public-road delivery robots that combine telemetry/autonomy with remote-operator fallback and has commercialized services in multiple jurisdictions. They pursue a hybrid teleoperation/autonomy strategy to expand real-world coverage quickly while managing regulatory and edge-case risk.
- Envimo — Envimo offers modular sidewalk robots targeting zero-emission urban deliveries; their small team and modular hardware approach enable low deployment cost and rapid customization for grocery and food retailers in constrained European neighborhoods.
- THEO — THEO fields semi-autonomous, human-monitored trike-sized robots with up to 100 kg payload capability, designed for bicycle-lane operation and campus/urban pilot programs. Their hybrid operational posture (human monitoring + automated navigation) reduces regulatory friction while supporting higher payload per vehicle than typical sidewalk bots.
- Ottonomy Inc — Ottonomy focuses on multi-compartment delivery robots with secure dispense mechanisms for unattended handoff and an emphasis on healthcare and residential verticals. Their platform highlights behavior-aware navigation to improve interaction safety in pedestrian environments.
Identify and analyze 391 innovators and key players in Autonomous Delivery more easily with this feature.
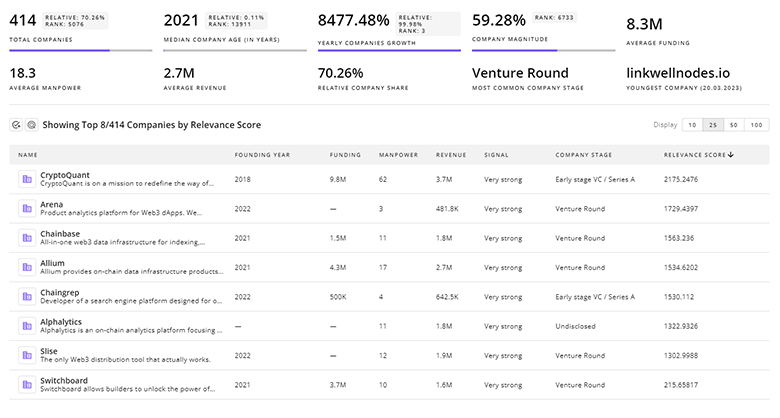
391 Autonomous Delivery Companies
Discover Autonomous Delivery Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Autonomous Delivery Investors
TrendFeedr’s investors tool offers a detailed view of investment activities that align with specific trends and technologies. This tool features comprehensive data on 1.1K Autonomous Delivery investors, funding rounds, and investment trends, providing an overview of market dynamics.
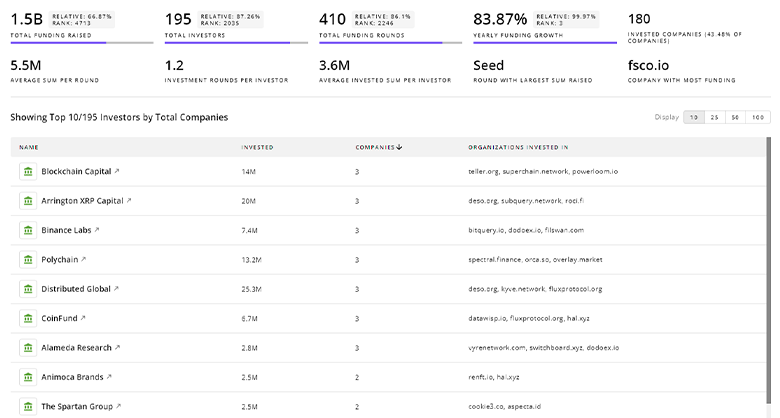
1.1K Autonomous Delivery Investors
Discover Autonomous Delivery Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Autonomous Delivery News
Stay informed and ahead of the curve with TrendFeedr’s News feature, which provides access to 3.4K Autonomous Delivery articles. The tool is tailored for professionals seeking to understand the historical trajectory and current momentum of changing market trends.
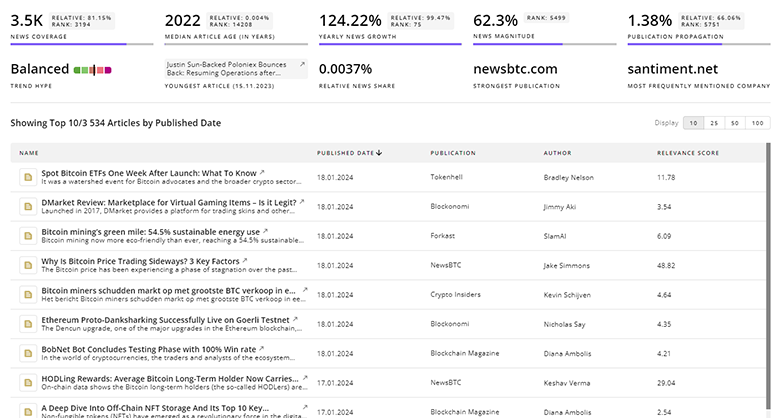
3.4K Autonomous Delivery News Articles
Discover Latest Autonomous Delivery Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Autonomous delivery has moved decisively beyond laboratory prototypes into segmented commercial operations. The most investible opportunities in the near term concentrate on niche routes and verticals where controlled environments or rigorous endpoint security make automation both feasible and profitable. Market forecasts vary, but internal trend data point to rapid expansion (from $1.85B in 2024 to $8.68B by 2029), which means businesses must convert pilots into repeatable service models now. Winners will be those that master hybrid operations (autonomy + teleoperation), integrate with micro-fulfillment networks, and treat the final customer handoff as a product requirement rather than an afterthought.
Interested in enhancing our coverage of trends and tech? We value insights from experts like you - reach out!