In-space Transportation Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe in-space transportation sector sits at a commercial inflection: total funding across companies working this topic reached $59.08B, underscoring material investor commitment to services that move payloads, people, and propellant inside Earth orbit and beyond. Market forecasts and industry commentary reinforce rapid revenue upside driven by rideshare and orbital-transfer demand, reusable launch programs, and nascent cislunar logistics, which together re-price the addressable opportunity for logistics-style businesses in orbit Space Transportation Market Size | Analysis Report – 2033.
The last update of this report was 147 days ago. If you spot incomplete or incorrect info, please let us know.
Topic Dominance Index of In-space Transportation
The Topic Dominance Index analyzes the time series distribution of published articles, founded companies, and global search data to identify the trajectory of In-space Transportation relative to all known Trends and Technologies.
Key Activities and Applications
- Last-mile orbital delivery (LEO/MEO/GEO). Operators build orbital transfer vehicles (OTVs) and space tugs that perform orbit-raising, plane changes, and final insertion — enabling rideshare economics and making small, cheaper satellites more useful; demand for GEO delivery is rising as operators seek direct-to-high-energy-orbit options.
- In-orbit servicing, refueling, and life-extension. Services that refuel, repair, and reposition satellites extend asset lifetime and convert one-off launches into recurring logistics revenue. Governments and primes now contract commercial ISAM capability studies and pilots, accelerating commercial deployments.
- On-orbit transfer and cargo logistics (space "freight" lanes). Modular payload adapters, standardized docking interfaces, and turn-key transfer vehicles enable scheduled cargo flows between platforms, depots, and surface ascent/descent nodes Orbital Transfer Vehicle Market.
- Earth return and frequent reentry for manufacturing & research. Reusable small reentry capsules and low-acceleration return vehicles enable commercial microgravity manufacturing and rapid sample return, closing the loop between in-orbit production and terrestrial markets.
- Debris mitigation and space sustainability services. Active deorbiting, tether systems, and rendezvous-and-capture servicing reduce collision risk and become a commercial requirement as orbital density grows.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Green propulsion moves from preference to procurement criterion. Operators and regulators prefer low-toxicity propellants (water, high-concentration hydrogen peroxide, iodine) because they reduce handling cost and regulatory friction; suppliers of flight-proven green thrusters therefore gain an early commercial advantage.
- Platformization of logistics and mission software. Firms that combine mission planning, STM/SSA, OTV scheduling, and standard interfaces capture higher-margin recurring revenue versus standalone hardware sellers; software platforms that simplify constellation ops accelerate adoption Leanspace.
- Hybrid propulsion stacks for operational flexibility. Systems combining chemical (high thrust) and electric (fuel efficient) engines enable faster transfers with lower mass penalty — a practical response to rideshare drop-off orbits and time-to-orbit SLAs.
- AI/autonomy becomes a revenue multiplier. Autonomous rendezvous, vision-based navigation, and ML for collision prediction reduce crewed intervention and lower ops cost; companies integrating AI into SDA/STM gain measurable reductions in collision alerts and maneuver overhead Neuraspace performance claims.
- Cislunar logistics trend is materializing. Plans and contracts for lunar propellant, depots, and dedicated transfer architectures move from concept to funded demonstrations, creating a new physical market beyond LEO ESA goals for reusable cadence and LEO logistics pilots.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Electric propulsion and high-ISP thrusters (Hall, ion, electrospray). These systems cut fuel mass for stationkeeping and long transfers, enabling OTVs and life-extension services.
- Green chemical propellants and water-based systems. Water and non-toxic monopropellant options simplify fueling infrastructure and safety compliance, reducing total cost of ownership for frequent servicing missions.
- Modular docking and refueling interfaces. Open, standardized mechanical and fluid interfaces (refuel plates, SIDRP-like concepts) enable a marketplace of refueling and servicing providers rather than bespoke one-off integrations OrbitAID refueling interface activity.
- Autonomous proximity operations and vision-based GNC. Onboard computer vision plus deterministic autonomy supports reliable capture, berthing, and payload transfer in crowded orbits Deneb Space autonomous navigation focus.
- Additive manufacturing for rapid, lighter components. 3D printing compresses development cycles for engines and tethers, lowers lead times and creates design options for reusable stages and service vehicles Additive Space Technologies use case.
- Electrodynamic tethers and propellantless options. Tethers offer deorbiting and low-energy stationkeeping with minimal consumables, differentiating sustainability offerings.
In-space Transportation Funding
A total of 396 In-space Transportation companies have received funding.
Overall, In-space Transportation companies have raised $61.2B.
Companies within the In-space Transportation domain have secured capital from 1.7K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of In-space Transportation companies over the last 5 years
In-space Transportation Companies
- ISPTech — ISPTech commercializes in-space propulsion spun out of a major propulsion research centre in Germany; it focuses on cost-effective, high-performance thrusters that fit cubesats through large satellites and emphasizes low-toxicity chemistries and extensive hot-fire test heritage. ISPTech targets operators that require flight-proven, low-handling-risk propulsion for last-mile orbit adjustments and stationkeeping.
- GATE Space — GATE builds plug-and-play mobility modules (the "Jetpack") that attach to satellite buses to provide on-demand delta-V without deep vehicle integration; the product lowers integration lead time and supports refueling with green propellants, positioning GATE as a quick-turn mobility supplier for constellation managers.
- Pale Blue — Pale Blue develops water-based propulsion systems aimed at cubesat-to-700 kg platforms; the water approach reduces handling hazards and improves supply chain simplicity for frequent missions, making it commercially attractive for operators adopting rideshare launch models.
- Orbital Paradigm — Orbital Paradigm focuses on low-mass, high-cadence return vehicles that enable frequent, low-G payload recovery; their Kestrel capsule targets microgravity manufacturers and research programs needing reliable Earth return without heavy manifest commitments.
- PERSEI Space — PERSEI pursues electrodynamic tether systems that provide propellantless deorbiting and station maintenance; their solution addresses debris mitigation and propellant cost exposure, making them a differentiated supplier to operators and sustainability-conscious customers.
TrendFeedr’s Companies tool is an exhaustive resource for in-depth analysis of 1.7K In-space Transportation companies.
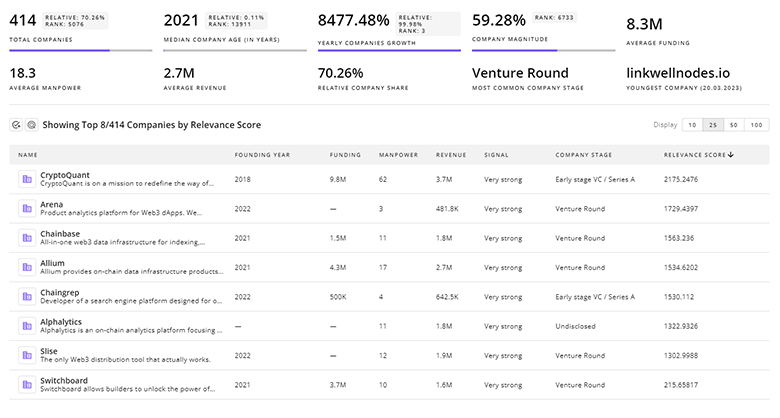
1.7K In-space Transportation Companies
Discover In-space Transportation Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
In-space Transportation Investors
The TrendFeedr’s investors tool features data on 2.4K investors and funding activities within In-space Transportation. This tool makes it easier to analyze complex investment patterns and assess market potential with thorough and up-to-date financial insights.
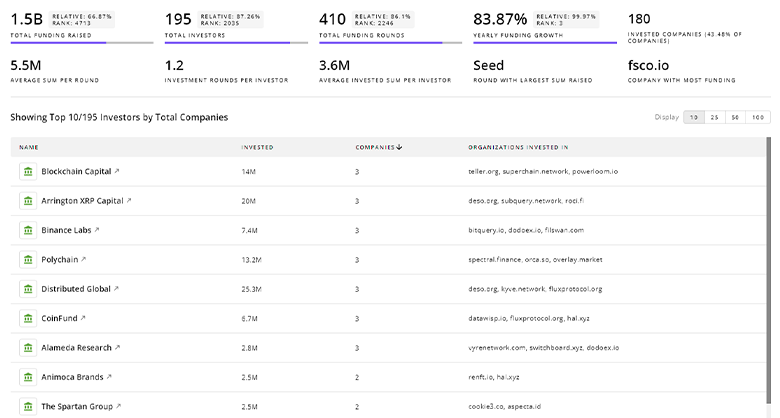
2.4K In-space Transportation Investors
Discover In-space Transportation Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
In-space Transportation News
Stay ahead of the curve with Trendfeedr’s News feature. The tool provides access to 5.9K In-space Transportation. Navigate the current business landscape with historical and current In-space Transportation data at your fingertips.
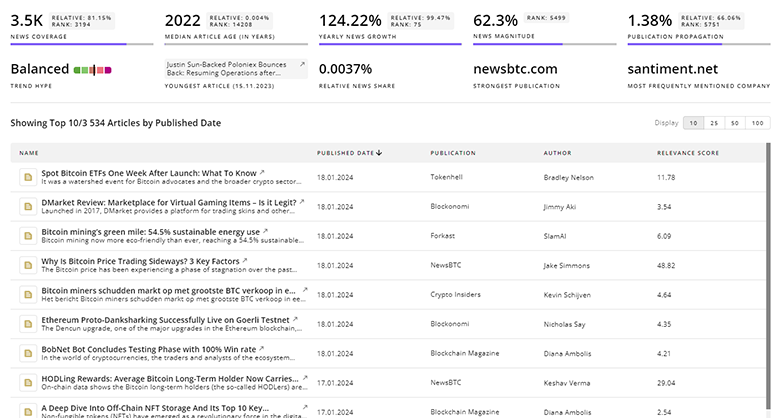
5.9K In-space Transportation News Articles
Discover Latest In-space Transportation Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
In-space transportation now reads as logistics and utilities work transplanted into orbital physics: investors fund many point technologies, but commercial value concentrates where software, standard interfaces, and refuelable mobility intersect to create repeatable service economics. The industry rewards providers that convert one-off mission hardware into subscription-able, schedule-driven services (OTVs, refueling, SSA/STM, and return logistics). Short-term winners will prove flight heritage for green and hybrid propulsion, demonstrate autonomous proximity ops at scale, and secure partnerships that embed their interfaces into end-to-end mission flows. Strategic players should therefore prioritize (1) standard interface adoption, (2) measurable operational cost reduction per maneuver, and (3) software-led scheduling and SSA services that turn discrete transfers into predictable, bookable logistics — because predictability and standardization convert technical capability into durable commercial cash flow.
If you’re an expert in trends or emerging tech, we invite you to contribute to our insights.










