Molecular Recycling Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe molecular recycling sector is shifting from pilots to industrial deployment, driven by policy and concentrated investment: projected capacity to process 20–25 million tons of plastic waste by 2030 and sector-wide investment commitments totaling $7,500,000,000 underpin growth expectations Chemical Recycling Market – Forecasts from 2025 to 2030. Markets interpret this as a selective scaling window—technologies that deliver virgin-equivalent feedstock at acceptable unit economics will capture the premium streams (textiles, food-grade PET, battery cathode precursors), while lower-cost thermal routes carve out volume-focused niches for mixed and low-grade wastes.
We last updated this report 3 days ago. Tell us if you find something’s not quite right!
Topic Dominance Index of Molecular Recycling
To gauge the impact of Molecular Recycling, the Topic Dominance Index integrates time series data from three key sources: published articles, number of newly founded startups in the sector, and global search popularity.
Key Activities and Applications
- Monomer recovery (PET/polyester depolymerization): Chemical routes recover BHET, PTA and analogous monomers for direct re-polymerization into food- and fiber-grade resins; this is the primary pathway for closing polyester loops.
- Textile molecular recycling (mixed-fiber deconstruction): Solvent- and microwave-assisted processes target blended garments to extract polyester monomers and preserve cellulose streams for re-use, enabling true textile-to-textile loops for apparel and technical fibers A polyester-dissolving process could make modern clothing recyclable.
- Advanced battery material rejuvenation: Direct-recycling and low-temperature hydrometallurgical processes recover high-purity cathode active materials at ~99.99% specification to feed EV supply chains and reduce dependence on mined feedstocks Battery recycling: 10 Breakthrough Technologies 2023.
- Solvent-based dissolution and selective purification: Dissolution techniques separate target polymers (e.g. multilayer films, polycarbonate) from contaminants to yield high-value feedstocks for packaging and specialty chemicals.
- Waste-to-feedstock (pyrolysis/gasification) for mixed plastics: Thermal conversion routes convert contaminated polyolefins into hydrocarbon feedstocks or syngas for petrochemical integration, yielding scale benefits but remaining cost-sensitive versus virgin feedstock The Global Advanced (Chemical or Feedstock) Recycling Market 2025-2040.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Policy is a demand lever: Extended Producer Responsibility and recycled-content mandates create guaranteed offtake pathways for chemically recycled grades, turning regulation into a near-term revenue mechanism for qualifying producers.
- Capital intensity concentrates winners: Plant capital intensity runs roughly $1,500–4,000 per ton of annual capacity; investors now favour near-commercial platforms with demonstrated plant economics rather than early-stage, high-uncertainty science.
- Biocatalysis is progressing from lab to market: Engineered enzymes and AI-driven variant discovery accelerate depolymerization performance and lower energy intensity for PET and nylon pathways, offering a potential low-CAPEX route to high-purity monomers A French company is using enzymes to recycle one of the most common single-use plastics.
- Traceability and verification matter: Molecular marking, digital passports and blockchain traceability are emerging as necessary tools to qualify recycled content for compliance and premium procurement, reducing counterparty risk in supply contracts.
- Value accrues to complexity handlers: Firms that economically process multilayer films, mixed textiles, and composite waste capture price premiums because these streams are excluded from conventional mechanical recycling and command higher margin arbitrage.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Glycolysis / Methanolysis (solvolysis): Targeted chemical depolymerization of PET and related polyesters to recover monomers at high purity for bottle- and fiber-grade production.
- Enzymatic depolymerization: Engineered PETase/MHETase families and thermostable variants enable depolymerization at lower temperatures and with narrower impurity profiles, reducing downstream purification burden.
- Microwave-assisted chemical recycling: Microwave energy accelerates depolymerization and reduces residence time, demonstrated in PET-focused processes that lower energy per kg of product.
- Catalytic pyrolysis / hydrothermal conversion / gasification: Thermal platforms convert mixed polyolefins into oils, syngas or chemical intermediates; they scale for volume but face competitiveness issues vs. virgin economics without policy support.
- AI-driven process control and digital feedstock qualification: Machine vision sorting, AI-enabled contamination detection, and digital traceability are becoming standard to secure consistent feedstock and protect catalyst life and product yields.
Molecular Recycling Funding
A total of 153 Molecular Recycling companies have received funding.
Overall, Molecular Recycling companies have raised $33.5B.
Companies within the Molecular Recycling domain have secured capital from 653 funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Molecular Recycling companies over the last 5 years
Molecular Recycling Companies
- Tereform — Tereform develops targeted molecular deconstruction processes for end-of-life textiles, focusing on converting mixed garments into pristine chemical building blocks for re-polymerization. The company positions itself as a supplier of feedstock for high-performance textiles and technical fibers rather than a commodity recycler, and it maintains early partnerships with apparel R&D groups to validate fiber-to-fiber loops.
- Evoralis — Evoralis supplies ultrahigh-throughput enzyme screening platforms that accelerate discovery of plastic-degrading biocatalysts by up to 1,000×, compressing the timeline from lab hits to process-ready variants. Their model targets enzyme optimization as a service to recyclers and chemical companies seeking reduced energy intensity in PET and other polyester routes.
- revalyu Resources GmbH — revalyu Resources commercialized a chemical PET bottle recycling process that produces rPET chips and resin intended for bottle-grade reuse; the firm reports industrial throughput and has been integrated by strategic acquirers to secure feedstock-to-polymer pathways The Global Market for Advanced Chemical Recycling.
- GR3N SA — GR3N applies microwave-assisted alkaline hydrolysis (DEMETO) to PET feedstock, claiming industrially viable depolymerization with reduced energy use and feedstock flexibility that includes textile inputs; their technology targets brand and polymer manufacturers seeking closed-loop PET.
- Composite Recycling — Composite Recycling focuses on reclaimed glass and carbon fiber recovery from FRP waste, producing reusable fibers and pyrolysis oil; this niche addresses high-value composite streams in aerospace and wind-turbine sectors that standard approaches cannot handle economically Next generation recycling of composites, technical fabrics and other textiles.
Enhance your understanding of market leadership and innovation patterns in your business domain.
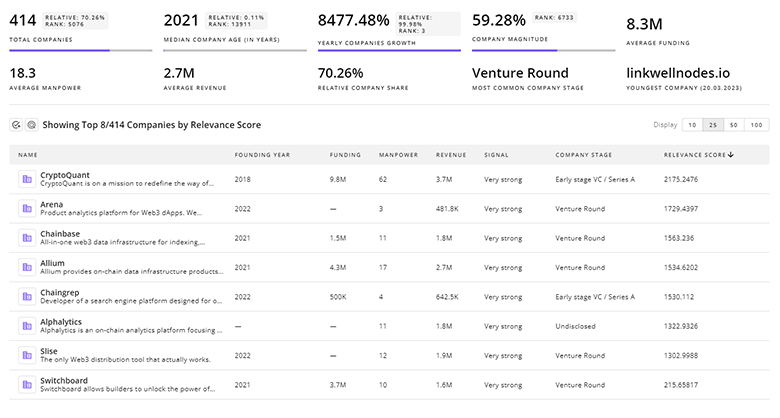
826 Molecular Recycling Companies
Discover Molecular Recycling Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Molecular Recycling Investors
TrendFeedr’s Investors tool offers comprehensive insights into 713 Molecular Recycling investors by examining funding patterns and investment trends. This enables you to strategize effectively and identify opportunities in the Molecular Recycling sector.
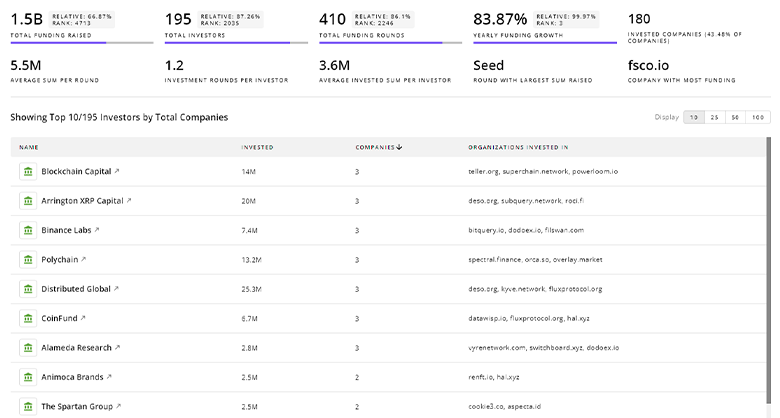
713 Molecular Recycling Investors
Discover Molecular Recycling Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Molecular Recycling News
TrendFeedr’s News feature provides access to 3.4K Molecular Recycling articles. This extensive database covers both historical and recent developments, enabling innovators and leaders to stay informed.
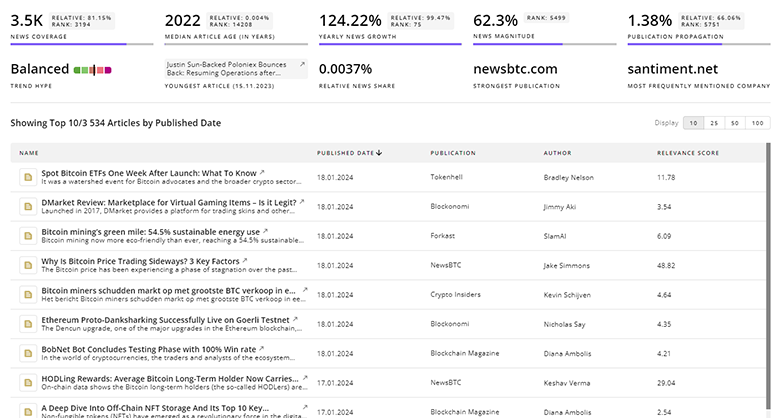
3.4K Molecular Recycling News Articles
Discover Latest Molecular Recycling Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Molecular recycling now plays a dual strategic role: it is a compliance lever that helps manufacturers meet recycled-content mandates and a source of premium feedstock for applications where material specification matters. The immediate winners will be organizations that secure verified feedstock, converge process IP with traceability, and demonstrate repeatable plant economics at scale. Investors and corporate buyers should prioritize partnerships with technology owners that minimize pre-treatment, reduce energy per kilogram of output, and validate product purity to food- or fiber-grade standards. In parallel, decentralized, lower-CAPEX deployments that handle local, contaminated streams will remain commercially attractive where logistics or trade restrictions constrain centralized supply. Firms that coordinate feedstock origination, digital verification, and process licensing will command the strategic advantage as the industry migrates from proofs of concept to sustained industrial throughput.
We value collaboration with industry professionals to offer even better insights. Interested in contributing? Get in touch!