Nuclear Energy Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe nuclear energy market sits at an inflection point where demonstrated demand and policy support meet new modular and fuel-cycle technologies; the internal data values the sector at about US$223.33 billion in 2023 and projects growth toward US$341.0 billion by 2032—a foundation that explains rising investor and government interest. Global capacity projections (high case) point to large-scale expansion—an additional 265 GW of capacity by 2040—creating concrete markets for SMRs, advanced fuels, and waste-consumption reactors that change where and how nuclear plants compete with variable renewables
We last updated this report 146 days ago. Tell us if you find something’s not quite right!
Topic Dominance Index of Nuclear Energy
To gauge the impact of Nuclear Energy, the Topic Dominance Index integrates time series data from three key sources: published articles, number of newly founded startups in the sector, and global search popularity.
Key Activities and Applications
- Large-scale fleet modernization and life-extension programs for existing reactors, driven by near-term capacity needs and favorable policy incentives that lower short-term supply risk.
- So what: extending existing assets buys time for advanced designs to reach commercial scale while preserving baseload reliability.
- Deployment of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) and microreactors for grid support, remote/off-grid power, and industrial heat; SMRs are framed as factory-built, scalable units that reduce FOAK financing pressure.
- So what: modular factory fabrication compresses schedules and creates repeatable cost learning curves, shifting investment risk from single large projects to serial production.
- Hydrogen and industrial process-heat integration (high-temperature electrolysis, thermochemical cycles) using advanced reactors, opening cross-sector revenues beyond electricity.
- So what: nuclear-to-hydrogen revenue streams materially improve project economics for reactors operating at elevated temperatures.
- Waste management, recycling, and closed fuel-cycle pilots (including reactors designed to consume spent fuel) to reduce radiotoxic inventory and extract energy value from legacy stockpiles.
- So what: solving long-term waste liability collapses a major political barrier and creates fuel-security value.
- Digitalization, AI, and predictive operations (digital twins, licensing acceleration tools) to increase availability and shorten regulatory friction.
- So what: reduced O&M and licensing costs improve unit economics and shorten time-to-market for new builds.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Policy-led capacity growth with quantifiable upside: high-case scenarios add ~265 GW by 2040, making nuclear an explicit decarbonization lever for many national strategies IAEA Raises Nuclear Power Projections for Fifth Consecutive Year.
- So what: clear policy intent lowers sovereign and offtaker risk, prompting new financing models (government guarantees, technology-neutral tax credits).
- SMRs poised to capture a material share of new capacity; the IEA and market forecasts highlight SMR deployment as a primary growth engine (SMR markets and forecasts in multiple reports) A new era for nuclear energy beckons as projects, policies ….
- So what: investors can size modular production lines and regional supply hubs rather than single EPC projects.
- Geographic concentration of new activity in Asia (China adding capacity rapidly) and selective European revival (life extensions, new builds) that shifts supply-chain sourcing and competitive dynamics World Nuclear Industry Status Report 2025.
- So what: buyers should plan dual sourcing and regional partnerships to manage trade or political risk.
- Growing private capital and corporate offtaker involvement (tech firms and utilities forming partnerships with reactor developers), changing project finance from sovereign-led to mixed public-private structures.
- So what: blended finance reduces the burden on utilities and accelerates FOAK demonstrations.
- Fusion receives accelerated private and public funding, creating a parallel R&D ecosystem whose medium-term advances (superconductors, AI for plasma control) will feed into commercial timelines and supply chains.
- So what: markets for high-field superconductors and specialized manufacturing will expand before commercial fusion power arrives.
Technologies and Methodologies
- SMRs and microreactors (factory-fabricated modules, transportable units) for distributed power and industrial applications.
- Strategic implication: modular manufacture enables industrial scaling and repetitive learning-curve cost reductions.
- Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs) and Integral Molten Salt Reactor (IMSR) family: options for high-temperature heat, long-fuel campaigns, and waste-consumption strategies Terrestrial EnergySeaborg Technologies.
- So what: MSRs target industrial heat markets and enable integrated hydrogen/desalination business cases.
- TRISO and HALEU fuel development to support Gen-IV and high-temperature reactors, improving safety margins and enabling higher burnup.
- So what: fuel suppliers and enrichment capacity become strategic bottlenecks worth investing in.
- Advanced fuel-cycle and waste transmutation (reactors designed to use spent fuel) that convert legacy liabilities into energy feedstock
- So what: successful demonstrations will materially reduce long-term storage cost assumptions in project models.
- AI, digital twins, and licensing automation tools to speed regulator interactions and reduce O&M costs
- So what: process automation compresses timeline risk, raising the present value of projects.
Nuclear Energy Funding
A total of 221 Nuclear Energy companies have received funding.
Overall, Nuclear Energy companies have raised $43.8B.
Companies within the Nuclear Energy domain have secured capital from 845 funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Nuclear Energy companies over the last 5 years
Nuclear Energy Companies
- Thorizon — Thorizon develops a modular molten salt reactor specifically designed to consume existing nuclear waste while producing 250 MW of electricity per unit; the company emphasizes cartridge-based cores for replaceability and circular fuel use. Thorizon's waste-to-energy positioning targets both environmental risk reduction and new revenue streams from fuel value recovery, which makes it a strategic partner for utilities holding large spent-fuel inventories. Its modular 250 MW concept aims to simplify siting and maintenance compared with large fleet plants.
- Dual Fluid — Dual Fluid advances a patented reactor that emphasizes converting nuclear waste into electricity and producing hydrogen and synthetic fuels; its design claims low land use and competitive levelized costs. The company frames its value as combining waste reduction with low-cost power for markets that need high temperature heat. If technical and licensing milestones are met, Dual Fluid could create new downstream industrial partnerships for heat-intensive sectors.
- Atomic Canyon — Atomic Canyon provides AI platforms for nuclear documentation, regulatory navigation, and plant operations data retrieval, starting with a nuclear-focused search and assistant toolset. Its approach addresses a critical friction point: regulatory complexity and document-intensive licensing. By reducing time and effort for licensing and compliance tasks, the company creates direct cost savings for developers and operators.
- Hadron Energy — Hadron Energy focuses on Micro Modular Reactor (MMR) units sized for 1–2 MW to serve data centers, remote industrial sites, and microgrids. The microreactor market targets customers with high reliability and limited grid access, offering a differentiated route to early commercial deployments and niche offtake contracts for data centers and mining operations.
- CAELUS — CAELUS develops AI-driven licensing and engineering assistant tools aimed at streamlining regulatory submissions and design documentation for reactor projects. By targeting the licensing bottleneck, CAELUS reduces the time and cost to move FOAK designs through regulatory gates—an enabling capability with disproportionate economic impact for first commercial deployments.
Enhance your understanding of market leadership and innovation patterns in your business domain.
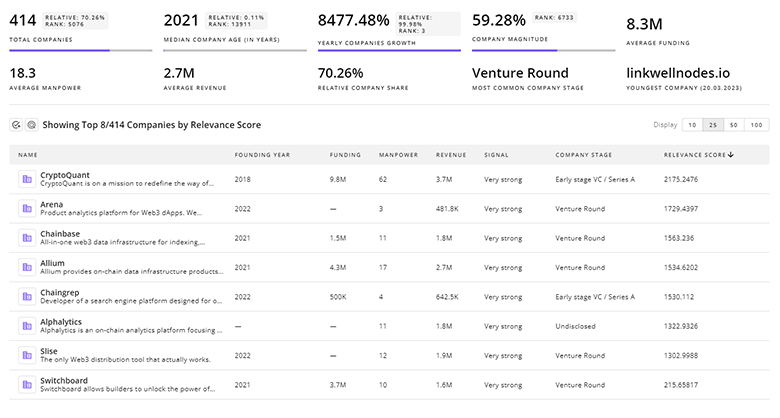
1.6K Nuclear Energy Companies
Discover Nuclear Energy Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Nuclear Energy Investors
TrendFeedr’s Investors tool offers comprehensive insights into 760 Nuclear Energy investors by examining funding patterns and investment trends. This enables you to strategize effectively and identify opportunities in the Nuclear Energy sector.
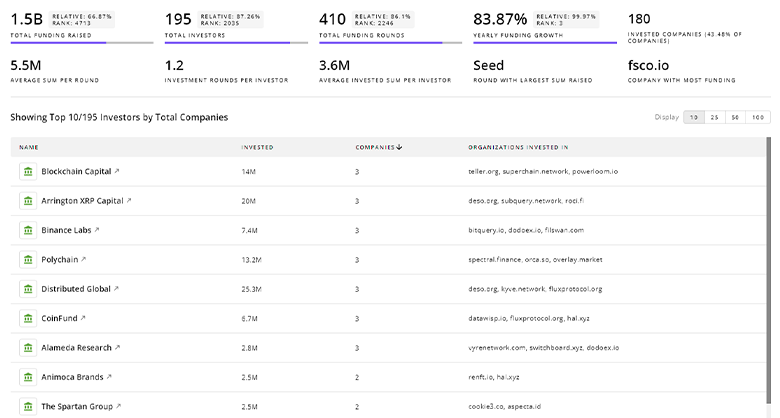
760 Nuclear Energy Investors
Discover Nuclear Energy Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Nuclear Energy News
TrendFeedr’s News feature provides access to 14.4K Nuclear Energy articles. This extensive database covers both historical and recent developments, enabling innovators and leaders to stay informed.
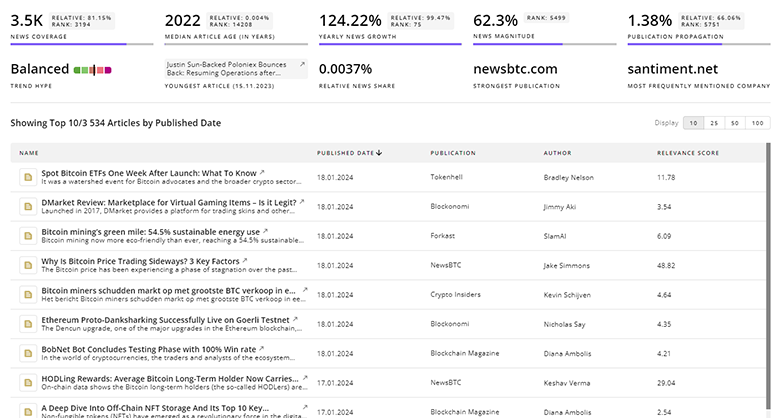
14.4K Nuclear Energy News Articles
Discover Latest Nuclear Energy Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Nuclear energy is shifting from policy rhetoric to executable market opportunities. The sector's current valuation and projected growth justify private and public investment across three linked tracks: (1) scale-out of modular, factory-fabricated SMRs and microreactors to meet near-term capacity and niche reliability needs; (2) commercialization of advanced fuel cycles and molten salt concepts that monetize waste and open industrial heat and hydrogen markets; and (3) digital and AI tools that compress licensing and operating costs. Investors and strategic buyers should prioritize assets that reduce FOAK risk—standardized module suppliers, HALEU and TRISO fuel supply chains, and licensing-automation services—while governments should focus incentives that convert policy intent into bankable projects. These coordinated moves will determine which companies capture lead positions as the sector moves into a phase of serial deployment and cross-industry integration.
We value collaboration with industry professionals to offer even better insights. Interested in contributing? Get in touch!











