Quantum Computing Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe quantum computing market is shifting from foundational research to application-driven deployment, with the 2025 market size recorded at $1,195,700,000 and an internal forecasted CAGR of 23.1%, signaling sustained commercial expansion as enterprise pilots scale into production pilots. This report integrates patent activity, company financials, market forecasts and vendor positioning to show that near-term value will flow from hybrid quantum-classical workflows, post-quantum security services, and quantum-ready optimisation platforms, while long-term value will concentrate where hardware scale, interconnectivity, and control-plane software converge.
This report was last revised 74 days ago. See a missing piece? Your input can help — contact us.
Topic Dominance Index of Quantum Computing
The Dominance Index for Quantum Computing delivers a multidimensional view by integrating data from three key viewpoints: published articles, companies founded, and global search trends
Key Activities and Applications
- Quantum cryptography and secure communications — migration planning for post-quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution are immediate enterprise priorities in finance, government and critical infrastructure.
- Hybrid quantum-classical optimisation for logistics and supply chains — firms are running pilot QUBO and QAOA-style workflows to reduce routing and scheduling costs where classical solvers struggle.
- Quantum simulation for drug discovery and materials — optimized variational algorithms and domain-specific circuit synthesis target molecular ground-state problems that classical methods approximate poorly.
- Quantum-as-a-Service (QaaS) and cloud access models — cloud deployment remains the primary enterprise access pattern, enabling cross-organization experimentation without heavy CAPEX on cryogenics or device ops.
- Control-plane and error-correction engineering — companies are commercialising low-latency decoders, pulse-level control and active noise-suppression stacks because practical advantage depends more on control quality than raw qubit count.
- Quantum-inspired classical solvers — physics-inspired and tensor-network emulators provide immediate ROI by delivering near-quantum performance for specific optimisation problems before fault-tolerant devices arrive.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Shift from qubit counts to control and orchestration. Recent patent and product activity shows firms prioritise error decoders, compilation that minimises circuit depth, and heterogeneous QPU scheduling, implying that control-plane IP becomes the primary value lever.
- Multi-modality parallelism. Superconducting, photonic, trapped-ion and neutral-atom approaches are each advancing complementary strengths (speed, room-temperature networking, fidelity, connectivity); enterprise strategy should treat modality diversity as a supply-chain and capability hedge.
- QaaS accelerates adoption but introduces governance friction. Cloud access grows adoption velocity while forcing enterprises to address latency, governance and job orchestration limits for regulated workloads.
- Post-quantum security is a budgeted real-world problem today. Organizations must treat harvest-now/decrypt-later risk as an active liability and invest in crypto-agility and migration plans Facing tomorrow's quantum hackers today.
- Market forecasts vary but consensus is strong growth. Conservative and aggressive market models place multi-year expansion above traditional tech growth rates; large public forecasts indicate wide investor and government commitment to scale (examples include multi-billion government pledges and multiple market forecasts projecting mid-30s CAGRs) Global Quantum Computing Market to Grow 34.6% - BCC Research.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Superconducting qubits and cryogenic electronics — mature in terms of control tooling and cloud availability; industry work also focuses on integrating digital control electronics into cryogenic stacks to reduce latency and operational cost.
- Photonic architectures for scale and interconnects — photonics aims for deterministic room-temperature interconnectivity and easier networking across modules, which supports modular scaling and quantum-network services.
- Neutral-atom systems and optical tweezer arrays — offer dense connectivity and straightforward scaling paths for some classes of problems, attractive for simulation and optimization workloads.
- Trapped-ion processors with high-fidelity gates — continue to lead on gate fidelity and reproducibility, enabling mixed workloads where per-gate quality drives accuracy.
- Variational and hybrid algorithms (VQE, QAOA, QML hybrids) — remain the principal mechanisms for extracting near-term value from NISQ devices via classical outer loops that optimize parametrized quantum circuits.
- Quantum error correction and decoder stacks — investment in qLDPC, surface-code toolchains and active decoders is concentrated among software-first firms and will shape which hardware architectures become commercially viable.
- High-fidelity classical emulation and quantum-inspired algorithms — tensor-network emulators and physics-informed solvers extend the utility of classical resources and de-risk enterprise investment while hardware scales.
Quantum Computing Funding
A total of 2.8K Quantum Computing companies have received funding.
Overall, Quantum Computing companies have raised $327.2B.
Companies within the Quantum Computing domain have secured capital from 9.5K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Quantum Computing companies over the last 5 years
Quantum Computing Companies
- Quantum Source — Quantum Source develops a photonic quantum architecture focused on deterministic photon-atom gates that aim to reduce system complexity and energy footprint versus alternative modalities. The company positions photonics as the path to fault tolerance through modular, networkable building blocks that simplify scaling. Its strategy targets enterprise verticals that need large-scale simulation and global entanglement distribution, supported by $77.00M in venture capital.
- Welinq — Welinq builds quantum interconnect hardware intended to make modular, multi-chip quantum systems practical by addressing high-bandwidth entanglement links and cryogenic interface design. The company's product focus reduces the dependency on monolithic qubit scaling by enabling distributed topologies that can be upgraded incrementally. Early grant funding and partnerships support rapid prototyping and testbed deployments.
- Miraex — Miraex offers photonic integrated circuit solutions for broadband entanglement distribution aimed at distributed quantum sensing, satcom and interconnect scenarios. By providing PIC-enabled entanglement routing and repeater components, the company targets both the quantum internet and multi-module quantum compute fabrics. Their seed funding of $9.75M supports engineering scale-up for entanglement-capable network nodes.
- SemiQon — SemiQon designs silicon-based quantum processors and cryo-optimised CMOS transistors so that quantum chips can be manufactured in conventional foundries. This strategy aims to lower per-qubit production cost and accelerate iteration cadence through standard semiconductor supply-chains. The company has raised $20.39M and is advancing device-level integration that directly addresses cryogenic packaging challenges.
- QDC — QDC - The Quantum Data Center Corporation delivers a hybrid solver and physics-inspired optimisation stack that allows enterprises to extract quantum-style improvements on routing and scheduling today. QDC's focus is on software-enabled optimisation that integrates with existing workflows, delivering immediate cost and efficiency gains while preparing clients for future QPU integration. QDC's product roadmap emphasises developer ergonomics and enterprise-ready APIs to reduce adoption friction.
TrendFeedr's Companies feature is your gateway to 22.9K Quantum Computing companies.
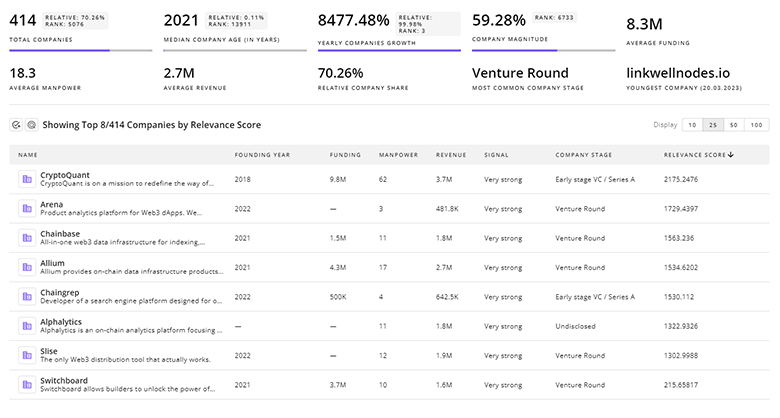
22.9K Quantum Computing Companies
Discover Quantum Computing Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Quantum Computing Investors
The Investors tool by TrendFeedr offers a detailed perspective on 9.4K Quantum Computing investors and their funding activities. Utilize this tool to dissect investment patterns and gain actionable insights into the financial landscape of Quantum Computing.
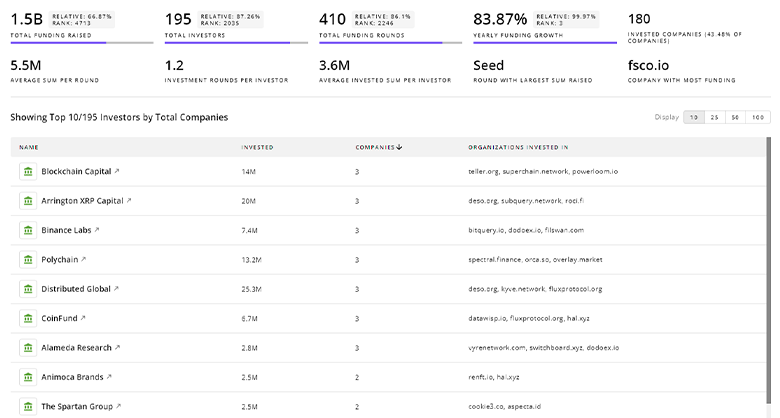
9.4K Quantum Computing Investors
Discover Quantum Computing Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Quantum Computing News
TrendFeedr’s News feature allows you to access 133.1K Quantum Computing articles as well as a detailed look at both historical trends and current market dynamics. This tool is essential for professionals seeking to stay ahead in a rapidly changing environment.
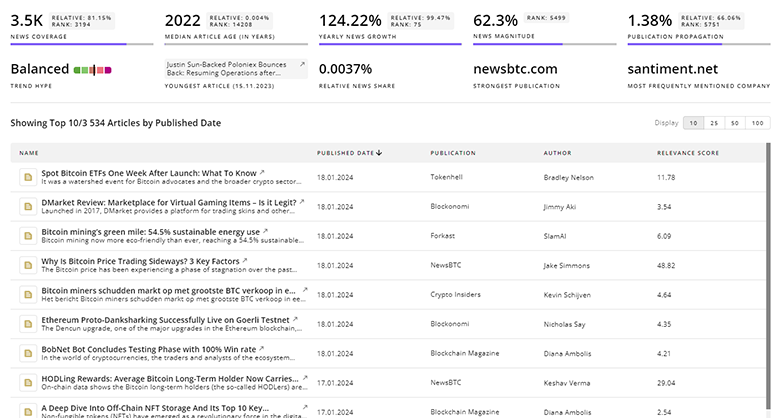
133.1K Quantum Computing News Articles
Discover Latest Quantum Computing Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
The quantum computing landscape now has two parallel, interacting objectives: capture near-term enterprise value through cloud-based services, quantum-inspired solvers and post-quantum security, while simultaneously investing in the control-plane and manufacturing pathways that enable large-scale, fault-tolerant systems. Strategic priorities for business leaders should be (1) secure crypto-agility and data governance to counter harvest-now/decrypt-later risk, (2) pilot hybrid quantum-classical workflows in high-value optimisation and simulation pockets with clear KPIs, and (3) form partnerships with companies that control control-plane IP or interconnect hardware because these layers will determine which hardware investments convert to commercial advantage. Organizations that combine pragmatic short-term deployments with targeted investments in orchestration and error-mitigation capabilities will preserve optionality and capture disproportionate value as the technology scales.
Partner with us to offer cutting-edge insights into trends and tech. We welcome your input.













