Space Exploration Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe space exploration landscape is shifting from episodic missions toward durable, serviceable infrastructure, driven by concentrated public budgets and private capital that are re-prioritizing logistics, autonomy, and resource access — exemplified by NASA’s Artemis program funding of *$24,000,000,000 in recent allocations*. Investment flows and program commitments now favor companies that provide repeatable delivery, in-space sustainment, and autonomous operations because those capabilities remove the biggest cost and schedule barriers to sustained lunar and deep-space activity.
45 days ago, we last updated this report. Notice something that’s not right? Let’s fix it together.
Topic Dominance Index of Space Exploration
To gauge the influence of Space Exploration within the technological landscape, the Dominance Index analyzes trends from published articles, newly established companies, and global search activity
Key Activities and Applications
- Lunar infrastructure and ISRU deployment — Designing landing pads, habitats, and regolith-based construction systems to reduce Earth-lift mass and mission cadence risk; capital commitments to habitat and surface demonstrations now shape procurement decisions.
- Commercial lunar transportation and logistics — Routine, contractable deliveries (cargo and payloads) to cis-lunar space are becoming a primary market; CLPS and similar government programs provide demand pull for repeatable service providers thebusinessresearchcompany - Lunar Exploration Market Insights, 2025.
- In-orbit servicing, refueling, and assembly — On-orbit fuel depots, servicing tugs, and autonomous assembly reduce lifecycle cost and enable modular mission architectures that scale across customers.
- Autonomous, distributed surface exploration — Swarms of cooperating robots and small rovers provide higher resilience and faster mapping than single large platforms, improving prospecting and scientific yield per mission.
- Space environmental intelligence and mission assurance — Continuous sensing of radiation, plasma, debris, and local terrain to reduce design margins and schedule risk for long-duration missions.
The industry is moving from "single mission success" to sustained operations supported by logistics, sensing, and autonomy — the business problem now is keeping assets productive in space, not merely getting them there.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Infrastructure-first economics — Investors and agencies prefer firms that control mobility and sustainment (launch-to-on-orbit transfer, depots, servicing). Market analysis shows infrastructure providers capture asymmetric value because they enable many downstream payload customers Grand View Research – Deep Space Exploration Market.
- Capital concentration behind repeatable services — Public budgets and institutional investors channel large sums into a smaller set of firms offering scalable services; total industry funding pools and program budgets are aligning to underwrite TRL advancement for such firms.
- Autonomy and multi-agent systems as competitive edge — Patent and mission activity indicate fast growth in cooperative robotic systems and onboard processing; companies that deliver low-latency, resilient autonomy gain operational leverage in deep-space and cislunar domains.
- Regulatory fragmentation creates operational arbitrage — Divergent national resource-extraction and commercial access laws create both compliance burdens and short-term market opportunities for firms that can structure cross-jurisdiction partnerships.
- Commercialization pathways are bifurcating — One track targets high-volume LEO/LEO-adjacent services (connectivity, smallsat mobility); the other focuses on high-value, low-frequency deep-space services (ISRU, planetary logistics). Firms that can bridge these tracks via modular offerings will be best positioned to scale thebusinessresearchcompany - Deep Space Exploration Market Insights, 2025.
Technologies and Methodologies
- Autonomous multi-robot coordination and edge processing — Onboard AI for real-time navigation, hazard avoidance, and collaborative mapping reduces reliance on Earth-side control and improves mission resilience at large light-time delay distances NASA CADRE research.
- In-space manufacturing and regolith-based construction — Additive manufacturing in orbit and regolith consolidation on the lunar surface lower launch mass and permit incremental expansion of habitats and landing infrastructure.
- Electric and advanced chemical propulsion for sustainable logistics — High-efficiency electric propulsion for smallsat mobility and higher-thrust chemical boosters for payload insertion create a layered propulsion ecosystem that optimizes cost per kilogram per mission.
- Environmental sensing stacks and predictive risk models — Miniaturized sensors plus cloud/AI analytics deliver predictive mission risk scores and allow margin compression in spacecraft design.
- Modular, repeatable logistics architecture — Standardized interfaces for docking, refueling, and payload integration enable an ecosystem of interoperable suppliers and turn single-use missions into service contracts.
Space Exploration Funding
A total of 696 Space Exploration companies have received funding.
Overall, Space Exploration companies have raised $50.4B.
Companies within the Space Exploration domain have secured capital from 2.6K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Space Exploration companies over the last 5 years
Space Exploration Companies
- Exploration Architecture Corporation — Focuses on lunar infrastructure by combining autonomous robotics with 3D printing processes that use regolith as feedstock; small team but targeted R&D (Lunatron™ and related systems) positions the company as an early supplier for surface construction services. Their approach reduces Earth-delivered mass and targets government and commercial payload customers seeking hardened landing surfaces.
- Orbit Beyond, Inc. — A lunar transportation and services firm that aims to provide versatile payload delivery in cis-lunar space and on the surface, leveraging CLPS program experience to build recurring commercial flight offerings; engineering focus is on extensible lander buses and logistics margins rather than single flagship missions.
- Space DOTS® — Builds smallspace environmental sensors plus an analytics layer to give mission designers high-fidelity, mission-specific environment data; their product reduces design margins and can materially lower earlier-stage risk in subsystem selection for long-duration missions.
- ThinkOrbital — An early-stage in-space construction and inspection firm that demonstrated autonomous welding in orbit and is developing X-ray inspection tools for on-orbit structural health monitoring; their capability set directly supports in-orbit servicing and modular assembly of large systems.
- Robotic Mining PTY LTD — A specialist in prospect mapping and high-throughput sampling concepts for lunar and Martian substrates, combining domain expertise in terrestrial mineral exploration with robotics and AI to accelerate resource prospecting and reduce geological risk for ISRU pilots.
Get detailed analytics and profiles on 3.9K companies driving change in Space Exploration, enabling you to make informed strategic decisions.
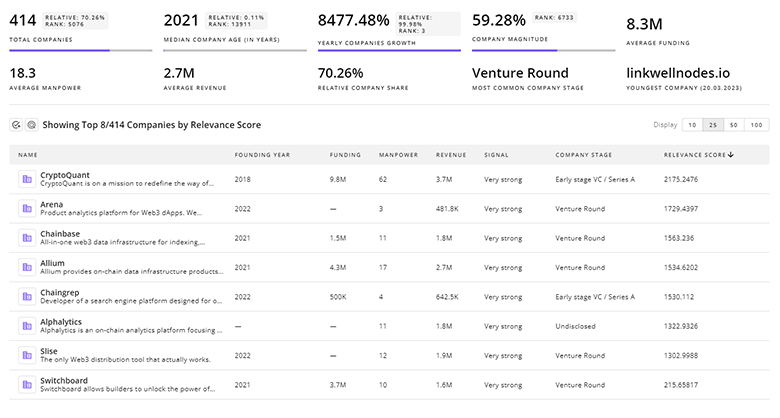
3.9K Space Exploration Companies
Discover Space Exploration Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Space Exploration Investors
TrendFeedr’s Investors tool provides an extensive overview of 3.3K Space Exploration investors and their activities. By analyzing funding rounds and market trends, this tool equips you with the knowledge to make strategic investment decisions in the Space Exploration sector.
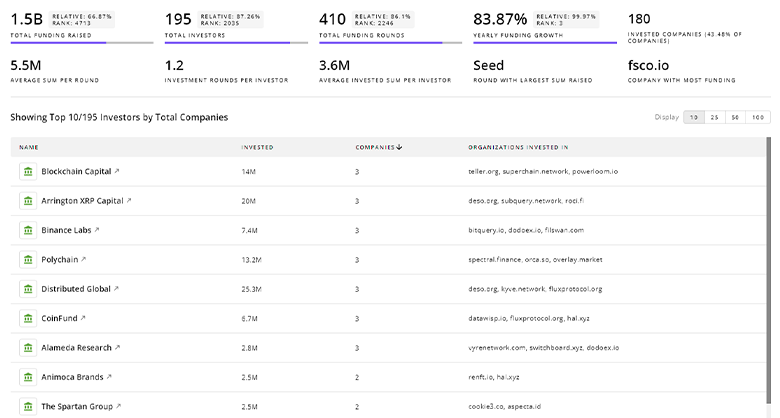
3.3K Space Exploration Investors
Discover Space Exploration Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Space Exploration News
Explore the evolution and current state of Space Exploration with TrendFeedr’s News feature. Access 47.4K Space Exploration articles that provide comprehensive insights into market trends and technological advancements.
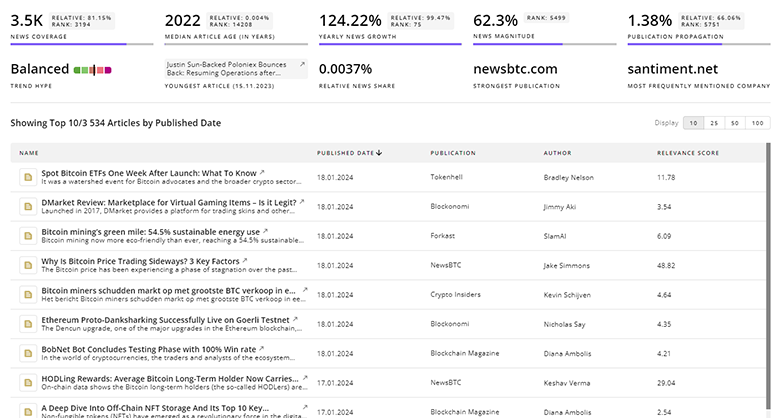
47.4K Space Exploration News Articles
Discover Latest Space Exploration Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
The immediate commercial opportunities in space exploration concentrate on making access reliable and assets productive: routine logistics, in-space sustainment, and autonomous operations create the economic plumbing that will let science, manufacturing, and resource markets scale. Firms that secure integration points in transport, refueling, and environmental intelligence gain asymmetric optionality because they convert episodic demand into recurring service revenue. For investors and corporate strategists, the pragmatic play is to fund and partner with companies that can demonstrate TRL progression for autonomy and ISM, deliver verifiable cost reductions in launch-to-service cycles, and provide interoperable interfaces that other firms can adopt as standards. Longer term, legal clarity on resource rights and coordinated traffic management will determine which commercial models survive; until those governance elements solidify, market winners will be those who can combine technical demonstration with durable revenue contracts.
We're looking to collaborate with knowledgeable insiders to enhance our analysis of trends and tech. Join us!