Zero Emission Bus Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe zero emission bus sector is at a measurable inflection: the internal trend data values the market at USD 42.64 billion in 2025 and projects USD 51.14 billion by 2029, implying continued, if moderate, expansion in core markets. Policy stimulus, falling battery-pack costs and system-level solutions (vehicle plus depot charging plus fleet software) drive procurement now; technology and infrastructure choices (battery vs hydrogen, depot vs opportunity charging, swapping) will determine which operators realise lower lifecycle costs and higher uptime.
5 days ago, we last updated this report. Notice something that’s not right? Let’s fix it together.
Topic Dominance Index of Zero Emission Bus
By combining normalized data from published articles, newly founded companies, and global search trends, the Topic Dominance Index provides a comprehensive lens that enables you to view the progression and prominence of Zero Emission Bus in relation to known Trends and Technologies.
Key Activities and Applications
Fleet electrification and repowering of legacy vehicles — transit agencies and school districts replace or retrofit diesel buses to reduce emissions and TCO; retrofit kits and repowering services accelerate near-term decarbonisation while spreading capital costs Strategic Profiling of European Bus OEMs, 2024–2030.
So what? Repowering reduces procurement lead times and enables agencies with constrained budgets to meet regulatory deadlines while deferring large-capex fleet replacement.Charging infrastructure deployment (depot fast chargers, pantographs, on-route opportunity chargers) — operators install high-power depot chargers and increasing numbers of pantograph systems for short dwell-time replenishment.
So what? Infrastructure timing and grid upgrades determine operational feasibility and cost profile; early planning reduces disruptive retrofit costs.Hydrogen fuel-cell deployments for long-range/high-utilisation routes — agencies trial FCEBs where fast refuelling and continuous operation outweigh current hydrogen supply economics.
So what? Hydrogen targets specific route profiles (intercity, coach, trunk corridors); adoption hinges on refuelling network rollout and green-hydrogen economics.Vehicle-to-grid and bidirectional energy services — pilot projects treat buses as distributed storage to provide grid services and monetise parked fleets during peak price periods Fermata Energy North America Electric Bus Market Size - By Bus….
So what? V2G creates new revenue lines, offsets energy costs and improves project IRR when integrated into procurement models.Data-driven fleet optimisation (telemetry, predictive maintenance, AI charging scheduling) — software platforms reduce energy consumption, prevent bus bunching and extend battery life Electric Bus OEM Lightweighting Strategies, 2024–2030.
So what? Digital tools convert hardware investment into measurable uptime and TCO improvements; they become a competitive differentiator for operators.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
Battery packs and energy management remain the locus of innovation and competition, with a parallel industry for battery packs and second-life uses emerging.
So what? Suppliers that can lower pack cost, improve thermal management and provide lifecycle services (recycling, second-life) will capture margin and reduce operator risk.Two-track propulsion strategy: BEBs dominate urban applications, FCEBs target long-range/high-utilization deployments; procurement increasingly mixes both depending on route profile Electric Mid- and Large Bus Market Technology Landscape….
So what? Fleet planners must segment networks and match propulsion to duty cycles; one-size-fits-all purchase strategies raise TCO.Platform and service business models (EaaS, BaaS, VaaS) gain traction — operators use subscription, battery-as-a-service or combined vehicle+charging contracts to lower entry barriers Highland Electric Fleets Growth Opportunities in the Electric Transit Bus and Coach Market, 2030.
So what? Operators move capex to opex; financiers with predictable revenue streams can accelerate fleet rollouts.Geographic and policy concentration drives deployment rhythm — China and parts of Europe lead manufacturing and deployments, North America grows rapidly with targeted incentives; quarterly registration volatility exists (e.g. Q1 2025 registration drop in some jurisdictions) CALSTART US ZEB adoption data ICCT quarterly snapshot Q1 2025 registration drop.
So what? Policy certainty (procurement mandates, grants) remains the single largest near-term determinant of fleet conversion timing.
Technologies and Methodologies
Advanced lithium-ion chemistries and scalable modular packs (including LFP and NMC variants) combined with improved BMS and liquid thermal management to protect performance in extreme climates.
So what? Chemistry choice affects upfront cost, safety profile, usable energy and second-life potential; procurement teams must evaluate chemistry vs duty cycle.High-power depot chargers, pantograph (opportunity) chargers and standardized interfaces to reduce dwell-time and avoid extensive grid upgrades Electric Bus Charging Technologies, Market Research coverage.
So what? Charging architecture sets route scheduling, depot footprint and grid reinforcement requirements.Battery swap and modular battery-as-a-service solutions for very high-utilisation fleets — demonstrated pilot concepts and early commercial pilots aim to reduce downtime Aulton.
So what? Swap models reduce charging peaks and capex exposure to battery depreciation but require standardisation and logistics investment.PEM fuel-cell stacks integrated into modular powertrains for coach/intercity service and hydrogen refuelling networks tied to renewables for low carbon intensity New Energy Bus Market – alliedmarketresearch.
So what? FCEB deployments scale only with coordinated hydrogen production and refuelling infrastructure investments.AI, telematics and digital-twin simulation for route-energy matching, predictive maintenance and charging orchestration Electric Bus Market – GMInsights on fleet digitalisation.
So what? These systems compress operational learning curves and unlock measurable energy and maintenance savings once integrated.
Zero Emission Bus Funding
A total of 56 Zero Emission Bus companies have received funding.
Overall, Zero Emission Bus companies have raised $21.4B.
Companies within the Zero Emission Bus domain have secured capital from 182 funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Zero Emission Bus companies over the last 5 years
Zero Emission Bus Companies
to zero electric vehicles GmbH — to zero focuses on retrofit kits and medium-duty bus repowering that shorten the lead time to transition fleets; their modular kits enable reuse of existing chassis while replacing the drivetrain and integrating a BMS, lowering purchase and disposal overheads. This model reduces immediate capital strain for agencies and fits routes with predictable duty cycles.
WattAnyWhere — WattAnyWhere supplies mobile and solar-augmented charging stations that allow operators to delay depot upgrades and trial electric fleets in constrained grid environments; their mobile chargers pair with renewable generation in pilot deployments to shave peak energy costs and accelerate pilots. By combining mobility and on-site generation they lower upfront grid reinforcement risk.
EVAnet — EVAnet develops interoperable depot charging networks and energy management software for mixed fleets; they emphasise load management and scheduling integration with fleet telematics to reduce peak demand charges and coordinate charging windows. Their platform makes multi-operator depots more cost effective.
BusGenius — BusGenius provides AI-based headway management and operational optimisation tools that reduce bus bunching and improve on-time performance; customers report lower energy consumption per route and better fleet utilisation after deployment. Their software helps capture the operational benefits that justify electrification investments.
TrendFeedr’s Companies feature offers in-depth knowledge on [number_of_companies] emerging companies defining the Zero Emission Bus landscape.
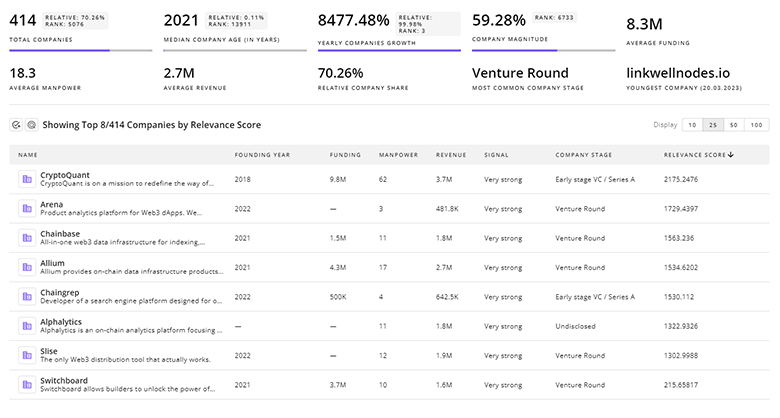
196 Zero Emission Bus Companies
Discover Zero Emission Bus Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
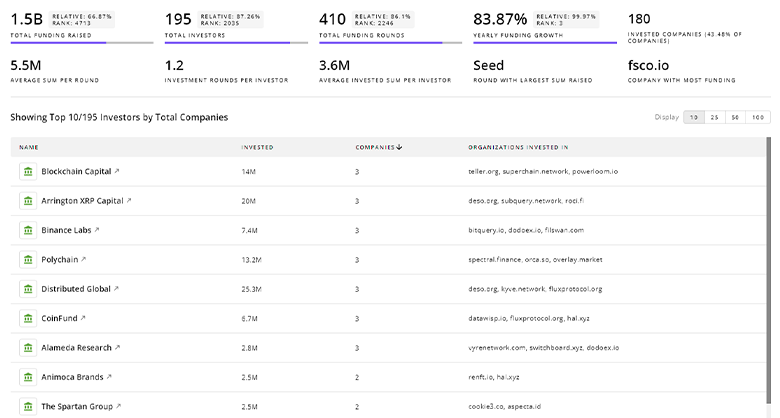
Zero Emission Bus Investors
TrendFeedr’s Investors tool enables you to navigate the investment landscape using the data on 166 Zero Emission Bus investors. It provides you with an in-depth analysis of funding rounds and investment trends to drive business strategies.
166 Zero Emission Bus Investors
Discover Zero Emission Bus Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
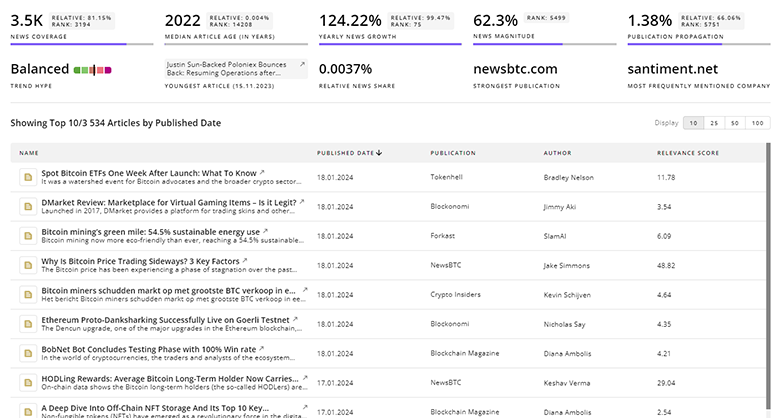
Zero Emission Bus News
Navigate the complexities of Zero Emission Bus with TrendFeedr’s News feature that offers access to 1.2K articles. This tool allows market analysts and strategists to stay informed about both past and present trends.
1.2K Zero Emission Bus News Articles
Discover Latest Zero Emission Bus Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
The zero emission bus sector now ties policy, technology and new commercial models into procurement decisions. Short-term success hinges on matching propulsion and charging architecture to route duty cycles, securing targeted incentives and structuring financing that shifts risk away from constrained agencies. Medium-term winners will be firms that integrate energy supply, battery lifecycle services and fleet software into cohesive offers that lower total cost of ownership and maintain uptime. For operators, the immediate priorities are (1) segment networks by duty cycle to select BEV or FCEB, (2) define depot charging architectures before bus orders, and (3) consider service models (EaaS/BaaS/VaaS) to manage capital exposure while capturing operational gains. These steps will convert policy momentum into reliable, financeable fleet transitions.
We're looking to collaborate with knowledgeable insiders to enhance our analysis of trends and tech. Join us!