Autonomous Navigation Report
: Analysis on the Market, Trends, and TechnologiesThe autonomous navigation market sits at an inflection point: hardware and sensor advances have reached commercial viability while navigation software and resilient PNT stacks now determine who captures scale. The market base is $7,060,000,000 in 2024, with a projected rise to $27,640,000,000 by 2030 and an internal CAGR estimate of 25.51%—figures that make commercialization and deployment speed the primary competitive levers. Market data and recent sector analyses indicate demand concentration in logistics, maritime automation, and GNSS-denied applications, creating immediate windows for companies that can deliver verifiable, integrable software stacks and sensor-agnostic redundancy layers marketsandmarkets – Autonomous Navigation Market Report, 2023.
This report was last updated 66 days ago. Spot an error or missing detail? Help us fix it by getting in touch!
Topic Dominance Index of Autonomous Navigation
To identify the Dominance Index of Autonomous Navigation in the Trend and Technology ecosystem, we look at 3 different time series: the timeline of published articles, founded companies, and global search.
Key Activities and Applications
- Logistics and Warehouse Automation — Development and deployment of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) for intra-warehouse transport, order fulfilment, and yard operations; these applications dominate short-term revenue capture because they reduce labor intensity and increase throughput.
- Last-mile and Mid-mile Delivery — Adaptive routing, teleoperation fallback, and mixed-fleet orchestration for urban delivery corridors; market reports identify land platforms as a fastest-growing commercial segment.
- GNSS-Denied & EW-Resilient Navigation — Alternative PNT solutions for contested or obstructed environments (magnetic, radar-based, visual-inertial, inertial fusion) used across defense, subterranean/indoor, and complex urban canyons; this is a strategic revenue channel with defense procurement tailwinds.
- Maritime Autonomy and Port Automation — Autonomous piloting, collision-avoidance co-pilots, and retrofit autopilots for existing fleets aimed at fuel optimization and crew reduction in busy ports.
- Aerial BVLOS and UTM Integration — Sense-and-avoid stacks, micro-radar detection, and airborne navigation that integrate into early UTM regimes to commercialize drone deliveries and inspections Autonomous Navigation Sensing System Market.
- Space & Extraterrestrial Navigation — On-board autonomy for satellites and lunar/planetary craft that reduces ground dependence and enables local decisioning for probes and constellations.
Emergent Trends and Core Insights
- Shift from Positioning to Decision Assurance — The intellectual property and product differentiation are moving from pure localization to how systems behave when position inputs degrade (failsafe planning, operational boundary management, human-machine handoff). This is reflected in available IP and product roadmaps in market briefs.
- Sensor-Agnostic, Software-First Platforms — Buyers prefer software stacks that absorb heterogeneous sensor inputs (camera, LiDAR, radar, inertial) and provide standardized APIs for OEMs and integrators; this reduces unit economics for specialized hardware and elevates middleware providers.
- Commercialization via Tiered Operational Domains — Companies are unlocking revenue by certifying autonomy in narrowly defined Operational Design Domains (ODDs) and then expanding; this minimizes regulatory friction while delivering demonstrable ROI in logistics and port use cases.
- Rapid Patent & Start-Up Activity, but Consolidating Value — There are 2,038 related patent records across the topic and heavy startup formation; yet capital distribution is skewed toward integrators and funded vertical specialists, implying acquisition pathways for ingredient innovators.
- Operational resiliency is an emergent buying criterion: customers pay a premium for systems that demonstrate graceful degradation and anti-spoofing/anti-jamming capabilities in field tests.
Technologies and Methodologies
- AI-augmented Sensor Fusion (VIO + LiDAR + Radar + IMU) — Multi-modal fusion engines that adapt sensor weighting in real time to preserve localization in adverse conditions; prioritized in product roadmaps and academic validation.
- Edge-first Compute & Deterministic Controllers — On-board inference (low latency) combined with Model Predictive Control (MPC) for safe trajectory execution under real-world constraints.
- High-Definition Map-Lite and Map-Free Navigation — Hybrid strategies that combine HD map anchors with map-free, perception-driven planners to reduce cost of map maintenance and improve performance in dynamic or temporary environments.
- Digital Twins and Simulation-First Validation — Automated synthetic scenario generation and fleet-level sim to accelerate verification and to close the sim-to-real gap before live pilots.
- Terrestrial & LEO-based PNT Augmentation — Complementary services (terrestrial 3D PNT, LEO augmentation) designed to improve integrity and availability where GNSS is unreliable NextNav (public).
Autonomous Navigation Funding
A total of 242 Autonomous Navigation companies have received funding.
Overall, Autonomous Navigation companies have raised $7.4B.
Companies within the Autonomous Navigation domain have secured capital from 1.0K funding rounds.
The chart shows the funding trendline of Autonomous Navigation companies over the last 5 years
Autonomous Navigation Companies
- Bavovna AI — Bavovna AI offers modular hardware plus SaaS AI navigation aimed specifically at GNSS-denied and electronic-warfare environments for aerial, surface, and subsurface vehicles; its dual-use product strategy targets defense contracts while enabling commercial uplift via software portability. The company is a small, venture-stage team (~50 employees) focused on modular, integrable stacks and stands out for its operational resilience focus.
- MSRS — MSRS builds PNT systems intended to deliver GPS-like fidelity in denied settings, originally designed by special-operations practitioners to remain functional under jamming. The firm is lean (~6 employees) and positions its patented solutions for tracked/wheeled platforms where military and critical infrastructure customers require rapid retrofit options.
- AstraNav — AstraNav pursues a software-only magnetic-field positioning approach (M-GPS®) that claims navigation without satellites, Wi-Fi, or extra hardware. The firm's value proposition is a device-scale, infrastructure-free navigation layer that can be embedded in phones and drones to provide always-available positioning in environments hostile to GNSS.
- Cambridge Sensoriis — Cambridge Sensoriis develops micro-radar and ARC (Active Radar Cooperating) localization tech targeted at BVLOS drones and dense air corridors; their micro-radars and radar-based localization provide satellite-independent, jamming-resilient positioning for airborne operations and wind-farm/utility inspections.
Identify and analyze 764 innovators and key players in Autonomous Navigation more easily with this feature.
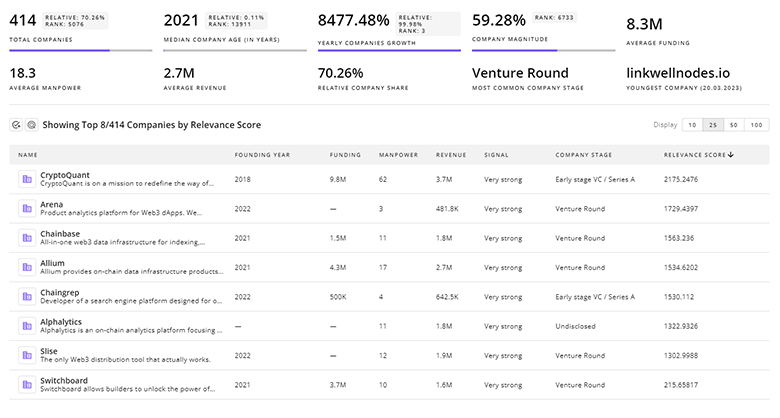
764 Autonomous Navigation Companies
Discover Autonomous Navigation Companies, their Funding, Manpower, Revenues, Stages, and much more
Autonomous Navigation Investors
TrendFeedr’s investors tool offers a detailed view of investment activities that align with specific trends and technologies. This tool features comprehensive data on 1.3K Autonomous Navigation investors, funding rounds, and investment trends, providing an overview of market dynamics.
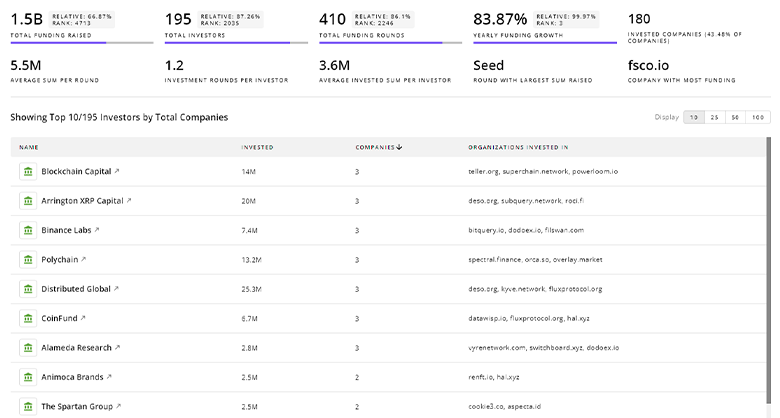
1.3K Autonomous Navigation Investors
Discover Autonomous Navigation Investors, Funding Rounds, Invested Amounts, and Funding Growth
Autonomous Navigation News
Stay informed and ahead of the curve with TrendFeedr’s News feature, which provides access to 2.4K Autonomous Navigation articles. The tool is tailored for professionals seeking to understand the historical trajectory and current momentum of changing market trends.
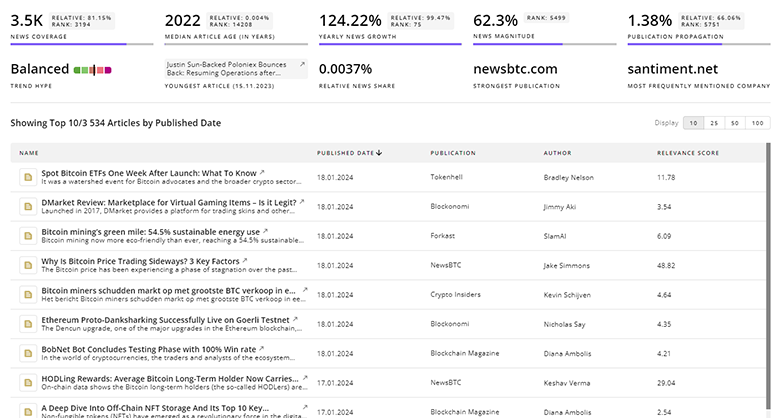
2.4K Autonomous Navigation News Articles
Discover Latest Autonomous Navigation Articles, News Magnitude, Publication Propagation, Yearly Growth, and Strongest Publications
Executive Summary
Autonomous navigation has shifted from a sensor-race to a systems-integration competition: success accrues to companies that deliver verifiable continuity of operation, clear ODD-based value cases, and standardized interfaces that let integrators drop software into heterogeneous fleets. Short-term commercial payoffs concentrate in logistics, ports, and GNSS-challenged safety-critical sectors; mid-term value flows to middleware and PNT augmentation providers that enable multi-domain resilience. Investors and strategic buyers should prioritize modular software platforms and validated field performance over bespoke hardware plays, and operators should require demonstrable failsafe behaviors and anti-spoof/anti-jamming capabilities as commercial procurement criteria.
Interested in enhancing our coverage of trends and tech? We value insights from experts like you - reach out!